Unpacking Iran's GDP Per Capita: A Deep Dive Into Economic Realities
The economic landscape of any nation is a complex tapestry woven from various threads, and for Iran, understanding its economic health often begins with a close examination of its Gross Domestic Product (GDP) per capita. This crucial metric offers a window into the average economic output and, by extension, the living standards of its citizens. Derived from data provided by reputable sources like the World Bank, analyzing Iran's GDP per capita reveals not just numbers, but the story of a nation navigating global economic shifts, internal policies, and geopolitical pressures.
In this comprehensive exploration, we delve into the nuances of Iran's GDP per capita, tracing its historical trajectory, scrutinizing recent figures, and comparing it against global benchmarks. We will distinguish between nominal and purchasing power parity (PPP) measures, explore the contributing sectors of its economy, and discuss the broader implications of these economic indicators. By dissecting these figures, we aim to provide a clear, accessible, and insightful overview for anyone interested in the economic realities of the Islamic Republic of Iran.
Table of Contents
- Understanding GDP Per Capita: The Basics
- Iran's GDP Per Capita: A Historical Perspective
- Recent Trends and Current Figures (2019-2024)
- Comparing Iran's GDP Per Capita to Global Averages
- Sectoral Contributions to Iran's Economy
- Overall GDP Growth and Projections
- Challenges and Influences on Iran's GDP Per Capita
- Looking Ahead: The Future of Iran's Economic Landscape
Understanding GDP Per Capita: The Basics
Before diving into the specific figures for Iran, it's essential to grasp what GDP per capita truly represents. This economic indicator is more than just a number; it's a fundamental measure used by economists and policymakers worldwide to gauge a nation's economic output and the prosperity of its citizens. Understanding its components helps in interpreting the data accurately and drawing meaningful conclusions about the economic health of countries like Iran.
- Weather Rasht Gilan Iran
- Breaking News Israel Attack Iran
- Iran Isreal War
- Qajar Iran
- Iran Attack Israel Map
What is GDP?
At its core, Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is the broadest quantitative measure of a nation's total economic activity. As defined by the World Bank, "GDP is the sum of gross value added by all resident producers in the economy plus any product taxes and minus any subsidies not included in the value of the products." In simpler terms, it's the total monetary value of all finished goods and services produced within a country's borders in a specific time period, usually a year. It encompasses everything from the cars manufactured to the services provided by a local barber, reflecting the overall scale of an economy.
Defining GDP Per Capita
While total GDP provides a snapshot of an economy's size, GDP per capita offers a more personalized view of economic output. The World Bank states that "GDP per capita is gross domestic product divided by midyear population." This calculation essentially distributes the total economic output evenly among every person in the country. Therefore, it serves as a proxy for the average standard of living and economic productivity of a nation's inhabitants. A higher GDP per capita generally suggests a more productive economy and, potentially, a higher quality of life for its citizens. Conversely, a lower figure can indicate economic struggles or a less developed economy. When we discuss Iran's GDP per capita, we are looking at this average economic share for each individual within the country.
Iran's GDP Per Capita: A Historical Perspective
To truly appreciate the current state of Iran's economy and its GDP per capita, it's crucial to look back at its historical performance. Economic data, especially over several decades, can reveal patterns, resilience, and the impact of significant events. The World Bank has provided estimates for Iran's GDP per capita since 1960, offering a rich dataset for analysis. This long-term view helps us understand the journey of Iran's economic output per person, highlighting periods of growth, stagnation, and decline.
Early Years and Peaks (1960-1976)
The journey of Iran's GDP per capita began in 1960 with a recorded low of $2,345.11 USD. However, the period leading up to the mid-1970s saw significant growth. On average, the GDP per capita in Iran averaged $4,435.95 USD from 1960 until 2023, indicating a fluctuating but generally upward trend over the very long term. A notable peak was reached in 1976, when the GDP per capita soared to an all-time high of $7,422.13 USD. This era, often characterized by significant oil revenues and ambitious development projects, saw considerable economic expansion, which translated into a higher average income per person. This historical peak serves as a benchmark against which later performances are often compared, illustrating a period of relative prosperity.
Decades of Fluctuation (1980-2024)
Following the peak in 1976, Iran's economic trajectory, and consequently its GDP per capita, entered a period of greater volatility. The post-1979 era, marked by geopolitical shifts, international sanctions, and internal economic policies, brought about considerable fluctuations. From 1980 to 2024, the GDP per capita rose by approximately $2.19 thousand U.S. dollars. This increase, while positive, masks periods of significant downturns and slow recovery. For instance, comparing the data with 2014, when the GDP per capita was $5,910, to more recent figures like $4,347 in 2023, shows a complex evolution. The average over the last decade (from 2014 to 2024) has been around $4,451 USD. This long stretch of data underscores the dynamic nature of Iran's economy and the various internal and external factors that have shaped its per capita output over the past four decades.
Recent Trends and Current Figures (2019-2024)
Focusing on the more immediate past provides critical insights into the current economic climate and the recent performance of Iran's GDP per capita. The period from 2019 to 2024 has been particularly dynamic, influenced by global events, commodity price fluctuations, and ongoing geopolitical factors. Analyzing these recent figures, primarily in current US dollars as provided by the World Bank, helps us understand the immediate challenges and any nascent recoveries.
The 2020 Decline
The year 2020 presented a significant challenge to economies worldwide, and Iran was no exception. Iran's GDP per capita for 2020 was recorded at $2,989 USD, representing a substantial 21.99% decline from the previous year, 2019. This sharp contraction can be attributed to a confluence of factors, including the global economic slowdown induced by the COVID-19 pandemic, which impacted oil demand and international trade, alongside the persistent pressure of international sanctions. Such a significant drop in a single year highlights the vulnerability of the economy to external shocks and the compounded effect of existing economic pressures on the average citizen's economic output.
2023 and 2024 Projections
Despite the challenges, more recent data suggests some degree of stabilization and even modest growth. The gross domestic product per capita in Iran was last recorded at $5,667.53 USD in 2023, a notable recovery from the 2020 low. This figure, provided by the World Bank, indicates a rebound in nominal terms. Looking ahead to 2024, the estimates suggest continued, albeit slow, improvement. The GDP per capita of Iran in 2024 was estimated at $4,430 (or €4,094), which is an increase of $315 (or €290) compared to the 2023 figure of $4,115 (or €3,804). It's also worth noting that in 2024, the GDP per capita in Iran was reported at $4,633 USD, compared to $5,910 in 2014 and $4,347 in 2023, as per other sources. These figures, while showing some year-on-year growth, also illustrate that the nominal GDP per capita has not yet surpassed the levels seen a decade ago in 2014, underscoring the long-term economic hurdles the nation faces in boosting its average economic output per person.
Comparing Iran's GDP Per Capita to Global Averages
Understanding Iran's GDP per capita in isolation provides only part of the picture. To truly gauge the economic standing and living standards within the country, it is essential to compare its figures against global averages. This comparison offers a benchmark, highlighting how Iran's economic output per person stacks up against the rest of the world. It also necessitates a discussion of two key measures: nominal GDP per capita and GDP per capita adjusted for Purchasing Power Parity (PPP).
Nominal Comparison
In nominal terms, which reflects current market prices and exchange rates, Iran's GDP per capita stands significantly below the global average. For instance, the gross domestic product per capita in Iran is equivalent to 45 percent of the world's average. More specifically, in 2023, the GDP per capita in Iran was reported at $4,466 USD, according to the World Bank collection of development indicators. When compared to the global average of $10,589 USD (as referenced for 2023), Iran's figure of $4,347 USD or $4,633 USD for 2024 indicates a considerable disparity. This gap suggests that, on average, the economic output per person in Iran, when measured in current US dollars, is less than half of the global average. This can impact international trade, investment, and the overall purchasing power of Iranian citizens when engaging with the global economy.
The Power of Purchasing Power Parity (PPP)
While nominal GDP per capita is useful, it doesn't fully account for the cost of living differences between countries. This is where Purchasing Power Parity (PPP) becomes invaluable. PPP adjusts for these differences, providing a more accurate picture of the real purchasing power of income within a country. When adjusted by purchasing power parity, the gross domestic product per capita in Iran was last recorded at $15,912.03 USD in 2023. This is a significant increase from the nominal figure and also an increase from $15,331 USD in 2022. This PPP-adjusted figure is equivalent to 90 percent of the world's average, which stood at $26,826 USD in 2023, based on data from 183 countries. Historically, the average for Iran from 1990 to 2023 in PPP terms is $12,746 USD, with a minimum of $9,047 USD in 1990 and a maximum of $15,912 USD in 2023. This demonstrates that while Iran's nominal GDP per capita may appear low, the actual cost of living and the purchasing power of its citizens' incomes are much closer to the global average, reflecting that goods and services are generally less expensive in Iran compared to many other parts of the world. This distinction is crucial for understanding the true economic well-being of the Iranian populace.
Sectoral Contributions to Iran's Economy
The overall GDP and, by extension, the GDP per capita of any nation are the sum of contributions from various economic sectors. Understanding which sectors dominate and how they evolve provides insight into the structure and resilience of the economy. For Iran, a nation often associated with its vast oil and gas reserves, the composition of its economic output reveals a more diversified picture than commonly perceived, though energy remains a critical component.
In the early 21st century, Iran's economic structure saw a significant shift towards services. The service sector emerged as Iran's largest contributor to GDP, encompassing a wide range of activities from finance, trade, and tourism to education and healthcare. This indicates a maturing economy moving beyond primary resource extraction and basic manufacturing towards more value-added activities. Following services, industry, which includes mining and manufacturing, played a substantial role. While oil and gas extraction are key components of the mining sector, manufacturing also contributes significantly, encompassing various industries from automotive to petrochemicals. Agriculture, traditionally a vital sector for food security and employment, followed as the third largest contributor. This diversification, even if partial, is crucial for long-term economic stability, as it reduces over-reliance on a single commodity or sector, thereby mitigating risks associated with price volatility or external shocks.
Historical estimates further illustrate the scale of Iran's economy. In 2008, Iran's GDP was estimated at $382.3 billion USD, or $842 billion USD when adjusted for purchasing power parity (PPP). This translated to a GDP per capita of $5,470 USD, or $12,800 USD in PPP terms for that year. By 2010, there were projections that the nominal GDP was expected to double in the next five years, indicating a period of optimistic growth forecasts. While actual outcomes can vary due to unforeseen circumstances, these figures highlight the significant economic base and potential that Iran possesses, driven by its diverse sectors and substantial natural resources. The interplay between these sectors is fundamental to the overall performance of Iran's GDP per capita.
Overall GDP Growth and Projections
Beyond the per capita figures, examining the total Gross Domestic Product (GDP) and its growth rates provides a broader context for Iran's economic performance. These aggregate numbers illustrate the overall expansion or contraction of the economy, which directly impacts the average output per person. Recent data from the World Bank offers a snapshot of these trends, revealing both challenges and periods of recovery.
In 2023, Iran's GDP was recorded at $401.50 billion US dollars. This figure represented a 2.88% decline from the previous year, 2022. This slight contraction indicates that while there might have been some per capita improvements in certain measures, the overall economic pie slightly shrank. However, looking back at 2022, Iran's GDP was $413.39 billion US dollars, which marked a significant 15.12% increase from 2021. This substantial growth in 2022 suggests a period of robust recovery or expansion, potentially driven by higher oil prices or increased production. Over the last decade, Iran has experienced an average real GDP growth of 2.8%, with some sources indicating an average of 2.3% over the same period. This indicates a moderate, albeit often volatile, growth trajectory for the overall economy. Such growth rates are crucial for sustaining improvements in the GDP per capita, as a growing economy generally means more resources to be distributed among the population. The fluctuations in total GDP underscore the sensitivity of Iran's economy to various internal and external factors, which in turn ripple down to affect the individual's share of the national output.
Challenges and Influences on Iran's GDP Per Capita
The trajectory of Iran's GDP per capita is not merely a reflection of internal economic policies but is profoundly shaped by a complex interplay of domestic and international factors. Understanding these challenges and influences is key to grasping the full picture of the nation's economic realities and the fluctuations observed in its per capita output.
One of the most significant and persistent influences on Iran's economy, and consequently its GDP per capita, has been international sanctions. These sanctions, primarily imposed by Western nations and the United States, have targeted Iran's oil exports, financial sector, and access to international markets. The direct impact is a reduction in revenue from its primary export (oil), making it harder to import essential goods, raw materials, and technology. This constrains industrial production, limits foreign investment, and can lead to currency depreciation, all of which depress economic activity and, by extension, the average income per person. The disparity between Iran's nominal GDP per capita (which is low compared to the world average) and its PPP-adjusted GDP per capita (which is much closer to the world average) can partly be explained by these sanctions, which distort exchange rates and make imported goods expensive, while local goods and services might remain relatively affordable.
Beyond sanctions, internal economic management, including fiscal and monetary policies, also plays a crucial role. Inflation, government spending, and efforts to diversify the economy away from oil have varying degrees of success and impact on the lives of ordinary citizens. Geopolitical tensions in the region and global oil price volatility are additional external factors that can cause significant swings in Iran's economic performance. A drop in oil prices, for instance, directly reduces government revenues and foreign exchange earnings, leading to austerity measures or a slowdown in development projects, ultimately affecting the GDP per capita. Conversely, periods of higher oil prices can provide a temporary boost. The ongoing need to manage these diverse pressures while striving for sustainable growth remains a central challenge for Iran in its quest to improve the economic well-being of its population.
Looking Ahead: The Future of Iran's Economic Landscape
Predicting the future of any economy is fraught with uncertainty, and for Iran, with its unique set of internal dynamics and external pressures, this is particularly true. However, by analyzing historical trends, current challenges, and the inherent strengths of the economy, we can offer some insights into the potential trajectory of Iran's GDP per capita.
The data clearly indicates that Iran possesses a substantial economic base and a diverse set of sectors, from a growing service industry to established manufacturing and, of course, its vast energy resources. The ability of the GDP per capita to rebound from lows, as seen from 2020 to 2023, suggests a degree of resilience within the economy. However, the persistent gap between its nominal GDP per capita and the global average, and the fluctuations in overall GDP growth, highlight the ongoing impact of external factors, primarily sanctions, and the need for robust internal economic reforms. Should there be a significant shift in international relations leading to the easing or lifting of sanctions, Iran's economy could experience a substantial boost, potentially accelerating the growth of its GDP per capita as foreign investment flows in and oil exports increase. This would unlock greater potential for development across all sectors, from infrastructure to technology, directly benefiting the average Iranian citizen.
Conversely, continued geopolitical tensions and the maintenance of sanctions would likely perpetuate the current pattern of moderate growth and volatility. In such a scenario, Iran would need to further emphasize domestic production, foster innovation, and continue diversifying its economy to mitigate external shocks. The focus on developing non-oil sectors, improving productivity, and enhancing the business environment will be crucial for sustained improvements in the GDP per capita. Ultimately, the future of Iran's economic landscape, and the well-being of its populace as reflected in their average economic output, will depend on a delicate balance of global geopolitical developments and the efficacy of internal economic strategies. The journey of Iran's GDP per capita remains a compelling narrative of resilience, challenge, and potential in the global economic arena.
Conclusion
Our deep dive into Iran's GDP per capita reveals a complex and dynamic economic narrative. From its historical peaks in the 1970s to the sharp decline in 2020 and subsequent modest recovery, the data from the World Bank paints a picture of an economy shaped by both internal policies and significant external forces. While Iran's nominal GDP per capita often lags behind the global average, its Purchasing Power Parity (PPP) adjusted figures show a much closer alignment, indicating a different reality for the purchasing power of its citizens within the country. The shift towards a service-dominated economy, alongside traditional industrial and agricultural sectors, underscores Iran's ongoing efforts to diversify its economic base.
Understanding Iran's GDP per capita is not just about numbers; it's about comprehending the economic realities faced by millions. This metric serves as a vital indicator of a nation's productivity and the living standards of its people. As Iran navigates its future, the evolution of its GDP per capita will remain a critical benchmark for its economic health and the prosperity of its population. We hope this comprehensive analysis has provided you with valuable insights into this crucial aspect of Iran's economy.
What are your thoughts on Iran's economic trajectory? Do you have any further questions or insights to share regarding its GDP per capita? Feel free to leave a comment below. For more in-depth economic analyses and country-specific data, we encourage you to explore other articles on our site.
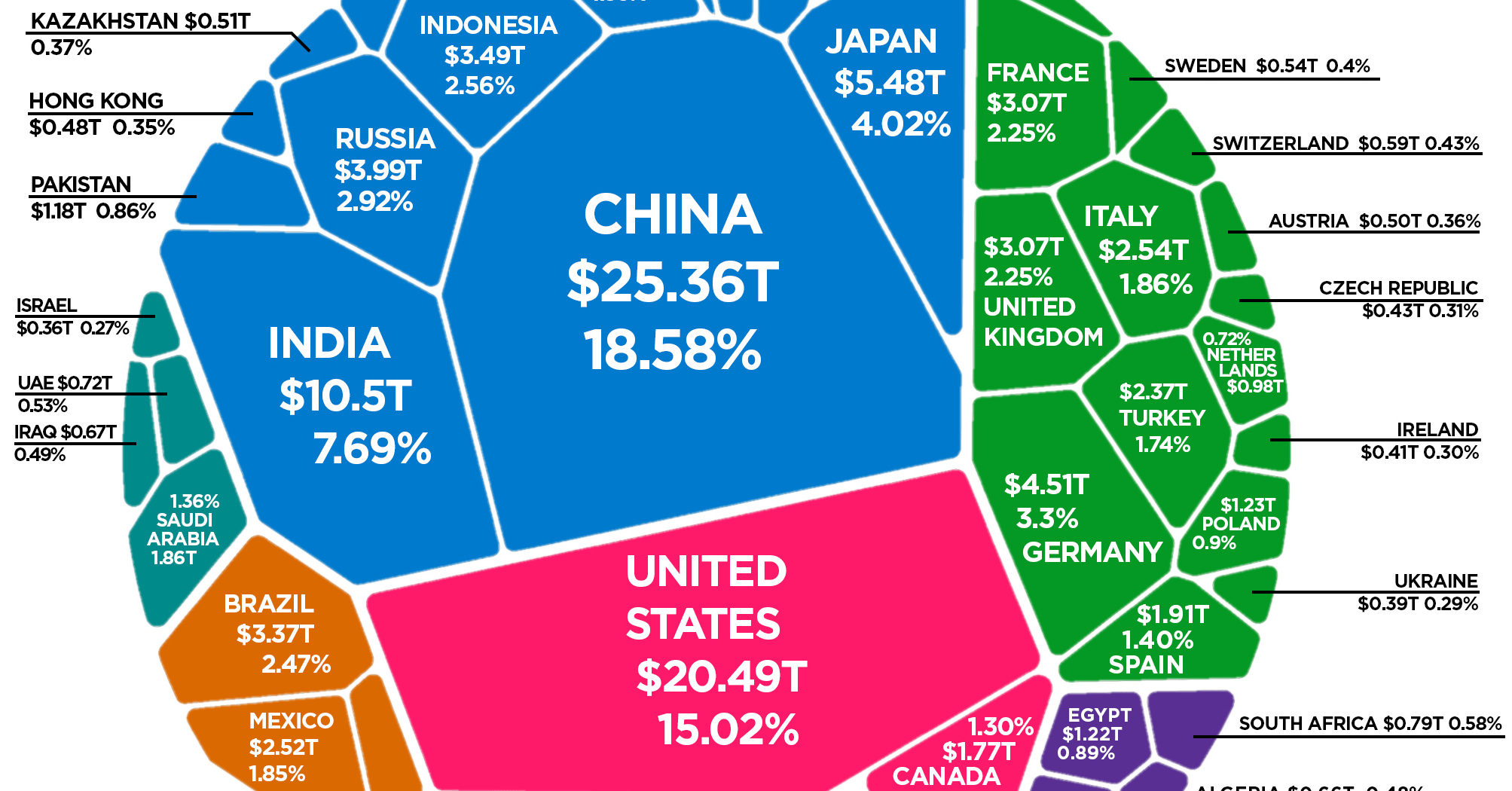
The Composition of the World Economy by GDP (PPP)
/gdp-increase-636251500-c69345ee97ba4db99375723519a2c1bd.jpg)
Real Gross Domestic Product (Real GDP) Definition

The World Economy in One Chart: GDP by Country