Unpacking Iran's GDP Per Capita: A Deep Dive Into Economic Health
Understanding the economic landscape of any nation requires delving into key indicators, and among the most crucial is Gross Domestic Product (GDP) per capita. For the Islamic Republic of Iran, this metric offers a window into the living standards and economic well-being of its population. Provided primarily by the World Bank, data on GDP per capita in Iran reveals a complex narrative of growth, decline, and resilience, shaped by a confluence of internal policies and external pressures. This article aims to meticulously explore Iran's GDP per capita, examining its historical trajectory, current standing, and future prospects, while providing a clear and accessible analysis for the general reader.
The journey through Iran's economic figures, particularly its GDP per capita, is not merely an academic exercise; it's an exploration of how a nation's wealth is distributed among its people and what that implies for their daily lives. By dissecting the nuances of nominal versus Purchasing Power Parity (PPP) figures, comparing Iran's performance against global averages, and identifying the driving forces behind these numbers, we can gain a comprehensive understanding of the challenges and opportunities facing the Iranian economy. This analysis, grounded in reliable data, is essential for anyone seeking to comprehend the true economic pulse of Iran.
Table of Contents
- Understanding GDP Per Capita: What Does It Mean?
- A Historical Overview of Iran's GDP Per Capita
- Iran's GDP Per Capita in Recent Years (Nominal US$)
- The Significance of Purchasing Power Parity (PPP)
- Iran's Economic Standing in Global Comparison
- Factors Influencing Iran's GDP Per Capita
- Challenges and Prospects for Iran's Economy
- The World Bank as a Key Data Source
Understanding GDP Per Capita: What Does It Mean?
Before diving into the specific figures for Iran, it's crucial to grasp what GDP per capita truly represents. At its core, Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is the total monetary or market value of all the finished goods and services produced within a country's borders in a specific time period. It's a comprehensive scorecard of a country's economic health. More precisely, GDP is the sum of gross value added by all resident producers in the economy plus any product taxes and minus any subsidies not included in the value of the products. This broad measure encompasses everything from manufacturing output to services, agricultural production, and government spending.
When we talk about GDP per capita, we are simply taking the total GDP and dividing it by the midyear population of the country. This division offers a crucial insight: it provides an average measure of economic output per person. While it doesn't reflect income distribution or individual wealth, it serves as a widely accepted indicator of the average standard of living and economic productivity within a nation. A higher GDP per capita generally suggests a more developed economy and, on average, a better quality of life for its citizens. Therefore, analyzing GDP per capita in Iran gives us a fundamental understanding of the nation's economic output relative to its population size, offering a proxy for the average prosperity experienced by its people.
A Historical Overview of Iran's GDP Per Capita
The economic journey of Iran, as reflected in its GDP per capita, has been marked by significant fluctuations over the decades. Data provided by the World Bank, covering the period from 1960 to 2023, paints a vivid picture of these shifts. Historically, the GDP per capita in Iran averaged 4435.95 USD from 1960 until 2023 in current US dollars. This long-term average, however, masks considerable volatility, reflecting periods of rapid growth, economic stagnation, and sharp declines.
Looking back, Iran's GDP per capita reached an all-time high of 7422.13 USD in 1976. This period, preceding the Islamic Revolution, was characterized by significant oil revenues and ambitious modernization programs. The country benefited from high global oil prices, which fueled economic expansion and investment. In stark contrast, the record low for Iran's GDP per capita was recorded at 2345.11 USD in 1960, at the very beginning of the World Bank's data collection for Iran. This initial low point highlights the nascent stages of its modern economic development.
The decades following the 1970s witnessed a more turbulent trajectory. Events such as the Iran-Iraq War (1980-1988), international sanctions, and periods of political and economic restructuring have profoundly impacted the nation's per capita output. These historical data points are not just numbers; they tell a story of a nation grappling with geopolitical challenges, internal reforms, and the fluctuating fortunes of the global energy market, all of which have directly influenced the economic well-being of its citizens. Understanding this historical context is vital for interpreting the more recent trends in GDP per capita in Iran.
Iran's GDP Per Capita in Recent Years (Nominal US$)
Focusing on the more contemporary period, Iran's GDP per capita in current US dollars has shown a dynamic pattern, reflecting both challenges and modest recoveries. According to the World Bank, the gross domestic product per capita in Iran was last recorded at 5667.53 US dollars in 2023. This figure, specifically, indicates that with a population of 90,608,707 people, the GDP per capita in the Islamic Republic of Iran was $5,668 in 2023. This represented a notable increase of $207 from $5,461 in 2022, signifying a change of 3.8% in GDP per capita.
However, the recent past also includes periods of significant contraction. For instance, Iran's GDP per capita for 2020 was $2,989, marking a substantial 21.99% decline from 2019. This sharp drop can largely be attributed to the compounding effects of severe international sanctions and the global economic slowdown induced by the COVID-19 pandemic. The recovery seen in 2022 and 2023 suggests a degree of resilience, with the overall GDP growth rate in 2023 recorded at 5.04%, representing a change of $24.662 billion over 2022, when real GDP was $488.865 billion.
Looking ahead, estimates for 2024 suggest that the GDP per capita in Iran was USD 4633. This compares to USD 5910 in 2014 and USD 4347 in 2023, indicating some variability in short-term projections depending on the source and methodology. Over the last decade, the GDP per capita in Iran averaged USD 4451. These figures, while showing a recent upward trend in nominal terms, still highlight the volatility and the long road ahead for sustained economic improvement and a higher average standard of living for the population. It's important to note that different World Bank series or estimates might present slightly varied nominal figures for the same year, such as another reported value of 4466 USD for 2023, but the general trend remains consistent.
The Significance of Purchasing Power Parity (PPP)
While nominal GDP per capita figures provide a straightforward comparison using current exchange rates, they don't always accurately reflect the true purchasing power of individuals within a country. This is where Purchasing Power Parity (PPP) comes into play. PPP adjustments account for differences in the cost of living and inflation rates between countries, allowing for a more accurate comparison of living standards. In essence, it answers the question: "How much would it cost to buy the same basket of goods and services in different countries?"
Using PPP, economists can create a more realistic picture of how much residents of a country can actually afford with their income. For nations like Iran, which have faced significant exchange rate volatility and sanctions, nominal figures can sometimes understate the actual economic well-being when compared to countries with stable, freely convertible currencies. Therefore, understanding Iran's GDP per capita in PPP terms is crucial for a comprehensive and nuanced evaluation of its economic strength and the real living standards of its population.
Iran's GDP Per Capita in PPP Terms
When adjusted by Purchasing Power Parity, the economic picture of Iran shifts significantly, often presenting a more favorable view of the average citizen's purchasing power. The latest value for the gross domestic product per capita in Iran, when adjusted by purchasing power parity (PPP), was last recorded at 15912.03 US dollars in 2023. This figure represents a substantial increase from 15331 US dollars in a preceding period, underscoring a growth in real terms.
Historically, the average for Iran from 1990 to 2023 in PPP terms is 12746 US dollars. The minimum value of 9047 US dollars was reached in 1990, while the maximum of 15912 US dollars was achieved in 2023, indicating a general upward trend in real purchasing power over the last three decades, despite intermittent challenges. Another World Bank collection of development indicators also reported GDP per capita, PPP (current international $) in Iran at 17660 USD in 2023, highlighting that different series or estimations might exist, but the overall PPP value is considerably higher than the nominal figures.
The comparison with global averages further illuminates Iran's position. While its nominal GDP per capita might appear modest on the world stage, its PPP-adjusted figure paints a different picture, suggesting a higher internal purchasing power. This distinction is vital for a holistic understanding of the economic realities facing the average Iranian citizen.
Iran's Economic Standing in Global Comparison
Placing Iran's GDP per capita figures in a global context provides essential perspective on its economic development and the living standards of its population relative to the rest of the world. When looking at nominal GDP per capita, the figures for Iran often appear significantly lower than the global average. For instance, the GDP per capita in Iran is equivalent to 45 percent of the world's average, based on the 2023 figure of 5667.53 US dollars. In comparison, the world average for current US dollar GDP per capita was approximately 19958.31 US dollars in 2023, based on data from 185 countries. This stark difference highlights the challenges Iran faces in terms of generating wealth at a comparable rate to many other nations, often due to external economic pressures and internal structural issues.
However, the narrative changes when we consider GDP per capita adjusted for Purchasing Power Parity (PPP). In this light, Iran's economic standing appears much stronger. The GDP per capita in Iran, when adjusted by purchasing power parity, is equivalent to 90 percent of the world's average. This is based on Iran's 2023 PPP figure of 15912.03 US dollars compared to the world average of 26826 US dollars, based on data from 183 countries. This significant difference between nominal and PPP comparisons underscores that while the nominal exchange rate might depress Iran's international economic standing, the actual cost of living and the purchasing power of its citizens internally are considerably higher than what nominal figures suggest.
Discrepancies in World Average Figures
It's worth noting that the "world average" figures provided in the data can vary. For example, some data points mention a global average of USD 10,589, while others cite 19958.31 USD or 26826 USD (for PPP). These discrepancies are typically due to several factors: the specific year the average is calculated for, the number of countries included in the calculation, and whether the average is for nominal GDP per capita or PPP-adjusted GDP per capita. For instance, the 10,589 USD average might refer to an earlier year or a specific subset of countries. When comparing Iran's figures, it is crucial to ensure that the world average used for comparison corresponds to the same year and the same type of GDP per capita (nominal or PPP) to maintain accuracy and provide a meaningful context. The most recent and detailed comparisons provided indicate Iran's nominal GDP per capita is significantly below the world average, while its PPP-adjusted GDP per capita is much closer, at around 90% of the global average.
Factors Influencing Iran's GDP Per Capita
The trajectory of GDP per capita in Iran is not a random walk; it is heavily influenced by a complex interplay of internal and external factors. Understanding these drivers is key to comprehending the nation's economic performance and its impact on individual living standards. The primary factors include global oil prices, international sanctions, domestic economic policies, and population dynamics.
The Role of Sanctions and Oil Prices
Perhaps the most dominant external factors shaping Iran's GDP per capita are international sanctions and the volatility of global oil prices. As a major oil producer, Iran's economy is highly dependent on oil exports for revenue. When oil prices are high and sanctions are eased, the country experiences an influx of foreign currency, which boosts government spending, investment, and overall economic activity, leading to an increase in GDP per capita. Conversely, periods of low oil prices or, more significantly, stringent international sanctions, severely restrict Iran's ability to sell its oil and access global financial markets. This leads to a sharp reduction in government revenue, a decline in investment, and often, high inflation and unemployment, which directly depress the GDP per capita. The 21.99% decline in Iran's GDP per capita in 2020 to $2,989 from 2019 serves as a stark reminder of the devastating impact of such pressures, compounded by the global pandemic.
Population Dynamics and Economic Growth
Beyond external factors, internal population dynamics also play a crucial role in determining GDP per capita. Given that GDP per capita is calculated by dividing total GDP by the midyear population, a rapidly growing population can dilute the per capita share of economic output, even if the total GDP is growing. Iran's population was approximately 90,608,707 people in 2023. While the country has experienced an average real GDP growth of 2.8% over the last decade (and 2.3% over another recent decade), the rate of population growth in relation to this economic expansion is critical. If economic growth outpaces population growth, per capita income tends to rise. If population growth is too rapid relative to economic expansion, it can put downward pressure on the average standard of living. Therefore, sustainable economic growth that creates sufficient opportunities and wealth for a growing population is essential for improving GDP per capita in Iran.
Other significant internal factors include the effectiveness of government economic policies, diversification efforts away from oil, investment in infrastructure and human capital, and the overall business environment. These elements collectively determine the nation's productive capacity and its ability to generate wealth for its citizens.
Challenges and Prospects for Iran's Economy
Despite recent signs of growth, the path forward for Iran's economy and its GDP per capita is fraught with both persistent challenges and potential opportunities. Understanding these aspects is crucial for a balanced view of the nation's economic future.
Key Challenges:
- Inflation: Chronic high inflation has been a significant issue in Iran, eroding purchasing power and creating economic instability. While PPP figures adjust for this to some extent, high inflation makes economic planning and daily life challenging for citizens.
- Unemployment: Particularly among the youth, high unemployment rates remain a pressing concern. A large, young, and educated population needs sufficient job opportunities to contribute to and benefit from economic growth.
- Economic Diversification: Despite efforts, the Iranian economy remains heavily reliant on oil revenues. This dependence makes it vulnerable to global oil price fluctuations and the impact of sanctions. A
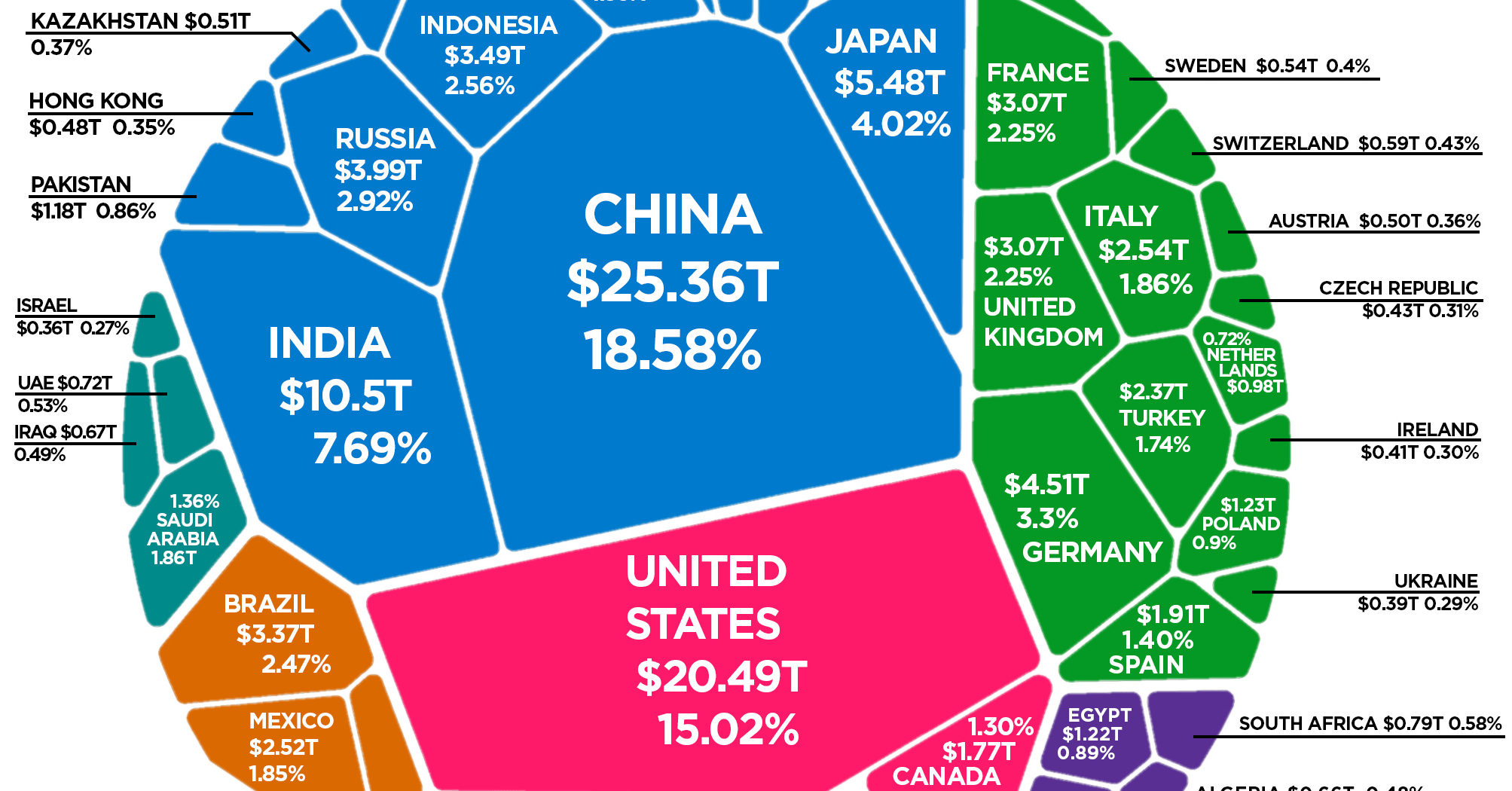
The Composition of the World Economy by GDP (PPP)
/gdp-increase-636251500-c69345ee97ba4db99375723519a2c1bd.jpg)
Real Gross Domestic Product (Real GDP) Definition

The World Economy in One Chart: GDP by Country