Iran's Economic Pulse: Unpacking GDP Per Capita Trends
Table of Contents
- What is GDP Per Capita? Defining the Core Metric
- Nominal vs. PPP: Understanding the Difference in Iran's GDP Per Capita
- A Historical Perspective: Iran's GDP Per Capita Journey Since 1960
- Recent Trends and Fluctuations: Iran's GDP Per Capita in the 2020s
- Iran's GDP Per Capita in Global Context: How Does It Compare?
- Sectoral Contributions to Iran's Economic Output
- Factors Influencing Iran's GDP Per Capita
- The Road Ahead: Implications and Outlook for Iran's GDP Per Capita
What is GDP Per Capita? Defining the Core Metric
Before delving into the specifics of Iran's economic figures, it's essential to grasp what GDP per capita truly represents. GDP stands for Gross Domestic Product, which is the sum of gross value added by all resident producers in the economy plus any product taxes and minus any subsidies not included in the value of the products. In simpler terms, it's the total monetary value of all finished goods and services produced within a country's borders in a specific time period, usually a year. When we add "per capita" to GDP, we are essentially dividing this total economic output by the midyear population. This gives us an average measure of economic output per person. It's a widely used indicator of a country's standard of living and economic well-being, providing a snapshot of how much economic value is generated, on average, for each individual in the population. While it doesn't account for income distribution or wealth inequality, it remains a powerful tool for comparing the economic productivity and prosperity levels between different countries or over time within the same country. The data for **GDP per capita for Iran**, Islamic Republic, is primarily provided by the World Bank, offering a consistent and reliable source for analysis.Nominal vs. PPP: Understanding the Difference in Iran's GDP Per Capita
When discussing **Iran's GDP per capita**, it's crucial to distinguish between nominal figures and those adjusted for Purchasing Power Parity (PPP). Both provide valuable insights, but they tell slightly different stories about the economy.Nominal GDP Per Capita in Iran
Nominal GDP per capita, often referred to as "current US dollars," represents the value of economic output per person at current market prices, without adjusting for inflation or differences in the cost of living between countries. This is the most straightforward measure. According to the World Bank, **GDP per capita in current US dollars for Iran, Islamic Republic**, has seen various fluctuations over the years. For instance, Iran's GDP per capita for 2020 was $2,989, marking a significant 21.99% decline from 2019. This drop highlights the immediate impact of global and internal economic pressures. More recently, the gross domestic product per capita in Iran was last recorded at $5,667.53 US dollars in 2023. Looking at projections, the GDP per capita of Iran in 2024 was estimated at €4,094 or $4,430, which was €290 or $315 higher than in 2023 (€3,804 or $4,115). This indicates a modest recovery or growth in nominal terms. Historically, the average **GDP per capita in Iran** averaged $4,435.95 USD from 1960 until 2023. It reached an all-time high of $7,422.13 USD in 1976 and a record low of $2,345.11 USD in 1960. These figures, primarily from the World Bank, illustrate the long-term economic journey of the nation. When compared globally in nominal terms, the GDP per capita in Iran is equivalent to approximately 45 percent of the world's average, based on 2023 data. In 2024, Iran's GDP per capita of $4,633 was significantly lower than the global average of $10,589.Purchasing Power Parity (PPP) GDP Per Capita
Purchasing Power Parity (PPP) adjusted GDP per capita offers a more realistic comparison of living standards between countries. It accounts for differences in the cost of goods and services, essentially asking how much local currency is needed to buy the same basket of goods and services in different countries. This makes it a better indicator of the actual purchasing power of individuals. The latest value for **GDP per capita, purchasing power parity**, for Iran from 2023 is $15,912 U.S. Dollars, an increase from $15,331 U.S. in the previous period. In comparison, the world average is $26,826 U.S. Dollars, based on data from 183 countries. Historically, the average for Iran from 1990 to 2023 is $12,746 U.S. The minimum value, $9,047 U.S. Dollars, was reached in 1990, while the maximum of $15,912 U.S. was recorded in 2023. When adjusted by purchasing power parity, the gross domestic product per capita in Iran was last recorded at $15,912.03 US dollars in 2023. This PPP-adjusted **GDP per capita in Iran** is equivalent to 90 percent of the world's average, a stark contrast to the nominal comparison. This suggests that while Iran's nominal income per person might appear lower, the cost of living allows that income to stretch further, providing a higher effective purchasing power relative to the global average than the nominal figures suggest. The World Bank also reported PPP (current international $) for Iran at $17,660 USD in 2023.A Historical Perspective: Iran's GDP Per Capita Journey Since 1960
Tracing the evolution of **Iran's GDP per capita** provides a fascinating glimpse into the nation's economic history, marked by periods of rapid growth, significant challenges, and remarkable resilience. Data from the World Bank allows us to graph and download economic data for constant GDP per capita for the Islamic Republic of Iran (NYGDPPCAPKDIRN) from 1960 to 2023, offering a consistent view of real economic output per person. As noted earlier, the average **GDP per capita in Iran** from 1960 until 2023 stood at $4,435.95 USD in nominal terms. The early years saw modest figures, with a record low of $2,345.11 USD in 1960. However, the mid-1970s marked a period of significant economic boom, largely fueled by rising oil prices. This culminated in an all-time high of $7,422.13 USD in 1976. This era reflects the impact of oil revenues on the national income and, consequently, on the per capita figures. The period following the late 1970s and early 1980s, encompassing the Iranian Revolution and the Iran-Iraq War, undoubtedly presented immense economic challenges, leading to significant declines in economic output and living standards. While specific year-on-year data for these periods isn't fully detailed in the provided text, the overall trend of averages suggests a complex recovery path. Looking at the PPP-adjusted figures, which are available from 1990, the average for Iran from 1990 to 2023 is $12,746 U.S. The minimum value in this PPP series, $9,047 U.S. Dollars, was reached in 1990, indicating the starting point of the PPP measurement period and the economic conditions at that time. The journey since then has seen fluctuations but generally an upward trend, reaching its maximum of $15,912 U.S. in 2023. From 1980 to 2024, the gross domestic product per capita in Iran, estimated at about $4.63 thousand U.S. in 2024, rose by approximately $2.19 thousand U.S. This long-term perspective highlights a gradual increase in economic output per person despite various internal and external pressures. Comparing the 2024 figure of $4,633 to $5,910 in 2014, and $4,347 in 2023, and an average of $4,451 over the last decade, it's clear that the path of **Iran's GDP per capita** has been characterized by both progress and periods of stagnation or decline, often influenced by global oil markets and geopolitical factors.Recent Trends and Fluctuations: Iran's GDP Per Capita in the 2020s
The 2020s have presented a dynamic and often challenging period for the global economy, and **Iran's GDP per capita** has been no exception. The data available paints a picture of both setbacks and signs of recovery in recent years. As previously mentioned, Iran's GDP per capita for 2020 was $2,989, representing a significant 21.99% decline from 2019. This sharp contraction can be attributed to a confluence of factors, including the global economic slowdown triggered by the COVID-19 pandemic and ongoing international sanctions that heavily impact Iran's oil exports and financial transactions. However, subsequent years have shown some rebound. Iran's overall GDP for 2022 was $413.39 billion US dollars, marking a 15.12% increase from 2021. While the overall GDP figure for 2023 saw a slight decline of 2.88% from 2022, settling at $401.50 billion US dollars, the per capita figures tell a nuanced story. In nominal terms, the gross domestic product per capita in Iran was last recorded at $5,667.53 US dollars in 2023. The World Bank also reported **GDP per capita (current US$) in Iran** at $4,466 USD in 2023. For 2024, estimates suggest a nominal GDP per capita of €4,094 or $4,430, which is an increase of €290 or $315 compared to 2023 (€3,804 or $4,115). This indicates a positive, albeit modest, upward trend in nominal terms for the immediate future. When considering the purchasing power parity (PPP) adjusted figures, the picture appears more robust. The latest PPP value from 2023 is $15,912 U.S. Dollars, an increase from $15,331 U.S. in the previous period. The World Bank's collection of development indicators compiled from officially recognized sources reported **GDP per capita, PPP (current international $) in Iran** at $17,660 USD in 2023. These PPP figures suggest that despite nominal fluctuations, the actual purchasing power of Iranians has shown a degree of stability and even growth in recent years, reflecting the internal dynamics of the economy and the cost of living. Comparing the 2024 estimated nominal GDP per capita of $4,633 to past figures, such as $5,910 in 2014 and $4,347 in 2023, and an average of $4,451 over the last decade, highlights the cyclical nature of Iran's economic performance. While the 2020 decline was significant, the subsequent years suggest a recovery, albeit one that is still navigating complex economic headwinds.Iran's GDP Per Capita in Global Context: How Does It Compare?
Placing **Iran's GDP per capita** within a global framework provides essential context for understanding its economic standing. Comparing its figures to world averages, both in nominal and purchasing power parity (PPP) terms, reveals different aspects of its economic strength and the living standards of its population. In nominal terms, the gross domestic product per capita in Iran is equivalent to approximately 45 percent of the world's average, based on 2023 data. This means that, on average, the economic output per person in Iran, when measured in current US dollars, is less than half of the global average. For instance, the GDP per capita of $4,633 in 2024 for Iran compares to a global average of $10,589. Similarly, in 2023, Iran's nominal GDP per capita of $4,347 was also significantly lower than the global average of $10,589. This gap highlights the challenges Iran faces in generating high per-person economic output in a globally competitive environment, often exacerbated by external pressures and reliance on volatile commodity markets. However, the picture changes significantly when we look at **GDP per capita, purchasing power parity**. As noted, the latest PPP value for Iran from 2023 is $15,912 U.S. Dollars. In comparison, the world average for PPP-adjusted GDP per capita is $26,826 U.S. Dollars, based on data from 183 countries. While still below the world average, the PPP-adjusted **GDP per capita in Iran** is equivalent to 90 percent of the world's average. This is a substantial improvement from the 45 percent figure seen in nominal terms. This significant difference between nominal and PPP comparisons underscores a critical point: the cost of living in Iran is generally lower than in many developed nations. This means that while the nominal income per person might be lower, the purchasing power of that income stretches further within Iran's borders. Therefore, the average Iranian's ability to acquire goods and services is closer to the global average than the nominal figures alone would suggest. This distinction is vital for a nuanced understanding of economic well-being and living standards. Furthermore, in terms of overall GDP, Iran ranks relatively high globally. The GDP figure in 2024 was estimated at €370,921 million or $401,357 million, placing Iran at number 41 in the ranking of GDP among the 196 countries for which data is published. This indicates a substantial overall economy, even if the per capita distribution, especially in nominal terms, lags behind the global average. The absolute value of GDP in Iran rose by €26,222 million or $28,537 million with respect to 2023, showing continued growth in the total economic pie.Sectoral Contributions to Iran's Economic Output
Understanding the composition of a nation's economy provides crucial context for its overall **GDP per capita**. For Iran, a country rich in natural resources, the contribution of various economic sectors has evolved over time, reflecting both inherent strengths and strategic shifts. In the early 21st century, the service sector emerged as Iran's largest contributor to the economy. This sector encompasses a wide range of activities, including finance, retail, healthcare, education, and tourism. The growth of the service sector is often a hallmark of developing economies as they mature, indicating a diversification away from purely primary industries. Following services, industry (mining and manufacturing) played a significant role. Iran possesses vast reserves of oil and natural gas, making its mining sector, particularly hydrocarbon extraction, a dominant force in its economy. The manufacturing sector, encompassing a variety of goods from automotive to petrochemicals, also contributes substantially. In 2008, Iran's GDP was estimated at $382.3 billion ($842 billion PPP), or $5,470 per capita ($12,800 PPP), with these sectors being key drivers. In 2010, the nominal GDP was projected to double in the next five years, indicating an ambitious growth trajectory for these industrial components. Agriculture, historically a foundational sector for many economies, follows industry in its contribution to Iran's GDP. Despite its arid climate in many regions, Iran has a significant agricultural sector producing a variety of crops and livestock. However, its relative share of the economy has diminished as other sectors have grown, a common trend in industrializing nations. The reliance on oil and gas exports has profoundly influenced **Iran's GDP per capita**. Fluctuations in global oil prices directly impact the nation's revenues, affecting government spending, investment, and ultimately, the economic well-being of its citizens. While there have been efforts to diversify the economy away from oil dependency, it remains a critical factor in Iran's overall economic performance and its per capita indicators. The interplay between these sectors, coupled with external factors, continuously shapes the trajectory of **Iran's GDP per capita**.Factors Influencing Iran's GDP Per Capita
The trajectory of **Iran's GDP per capita** is shaped by a complex interplay of internal and external factors, ranging from geopolitical dynamics to domestic economic policies and natural resource endowments. Understanding these influences is key to interpreting the past and anticipating future trends. One of the most significant external factors impacting Iran's economy and, by extension, its GDP per capita, is international sanctions. These sanctions, primarily imposed by Western nations due to Iran's nuclear program and other geopolitical considerations, have severely restricted Iran's ability to export oil, access international financial markets, and import essential goods and technologies. The decline in oil revenues directly impacts government spending, investment in infrastructure, and the overall economic activity, leading to lower per capita output. The sharp 21.99% decline in **Iran's GDP per capita** from 2019 to 2020, for example, can be largely attributed to the intensification of these sanctions and the concurrent global economic slowdown. Global oil prices also play a crucial role. As a major oil producer, Iran's economy is highly sensitive to fluctuations in crude oil prices. Higher prices typically translate to increased government revenues, which can be reinvested in the economy, boosting growth and potentially increasing GDP per capita. Conversely, a drop in oil prices can lead to economic contraction. The all-time high of $7,422.13 USD in **Iran's GDP per capita** in 1976 was largely a reflection of the oil boom of that era. Domestic economic policies, including fiscal management, monetary policy, and efforts towards economic diversification, also significantly influence per capita income. Policies aimed at fostering non-oil sectors, promoting private investment, and improving the business environment can help stabilize and grow the economy, making it less vulnerable to external shocks. Inflation, often a persistent challenge in Iran, erodes purchasing power and can mask real economic growth, making PPP-adjusted figures particularly important for understanding true living standards. Population growth is another demographic factor. Since GDP per capita is calculated by dividing total GDP by the population, a rapidly growing population can dilute the per capita figure even if the overall GDP is increasing. Effective population management and ensuring that economic growth outpaces demographic expansion are vital for sustainable improvements in **Iran's GDP per capita**. Finally, internal stability, regional conflicts, and the country's integration into the global economy through trade and foreign direct investment are all critical determinants. A stable political and social environment is conducive to investment and economic activity, while regional tensions or isolation can deter it. All these elements combine to create the complex economic environment that shapes the financial well-being of the average Iranian.The Road Ahead: Implications and Outlook for Iran's GDP Per Capita
The journey of **Iran's GDP per capita** has been one of significant ups and downs, reflecting a nation grappling with both internal complexities and external pressures. As we look ahead, the implications of these trends are profound for the Iranian populace and the global economic landscape. The persistent gap between Iran's nominal GDP per capita and the world average, while partially mitigated by its lower cost of living as shown by PPP figures, highlights the ongoing challenge of achieving broad-based prosperity. While the recent increases in both nominal and PPP **GDP per capita in Iran** are encouraging signs of recovery from the 2020 decline, the path to sustained, high growth remains intricate. The average real GDP growth of 2.8% over the last decade (or 2.3% in another measure) suggests a modest but consistent expansion, yet one that needs acceleration to significantly elevate living standards. For the average Iranian, the trajectory of GDP per capita directly translates to their quality of life, access to goods and services, and overall economic opportunities. Improvements in this metric, especially in PPP terms, mean that people can afford more, even if their nominal incomes don't seem globally competitive. However, the underlying factors, such as inflation and unemployment, which are not directly captured by GDP per capita, also play a crucial role in daily economic realities. The outlook for **Iran's GDP per capita** will largely depend on several key factors. The future of international sanctions remains paramount; any easing or lifting of these restrictions could unlock significant economic potential, particularly in the oil and gas sectors, and facilitate greater foreign investment and trade. Furthermore, domestic policies aimed at economic diversification, fostering a vibrant private sector, improving productivity, and managing inflation will be crucial for sustainable growth. Investments in human capital, infrastructure, and technology will also be vital for enhancing the country's productive capacity and, consequently, its per capita output. In conclusion, **Iran's GDP per capita** is more than just an economic statistic; it's a barometer of the nation's economic health and the well-being of its people. While the data from the World Bank and other sources paints a picture of resilience and gradual recovery, the journey ahead is complex. Continuous monitoring of these figures, alongside other socio-economic indicators, will be essential to understand the evolving narrative of Iran's economy and its impact on its citizens. We hope this comprehensive analysis of **Iran's GDP per capita** has provided you with valuable insights. What are your thoughts on Iran's economic future? Share your perspectives in the comments below! If you found this article informative, please consider sharing it with others who might be interested, and explore our dedicated page for more in-depth economic data and analyses.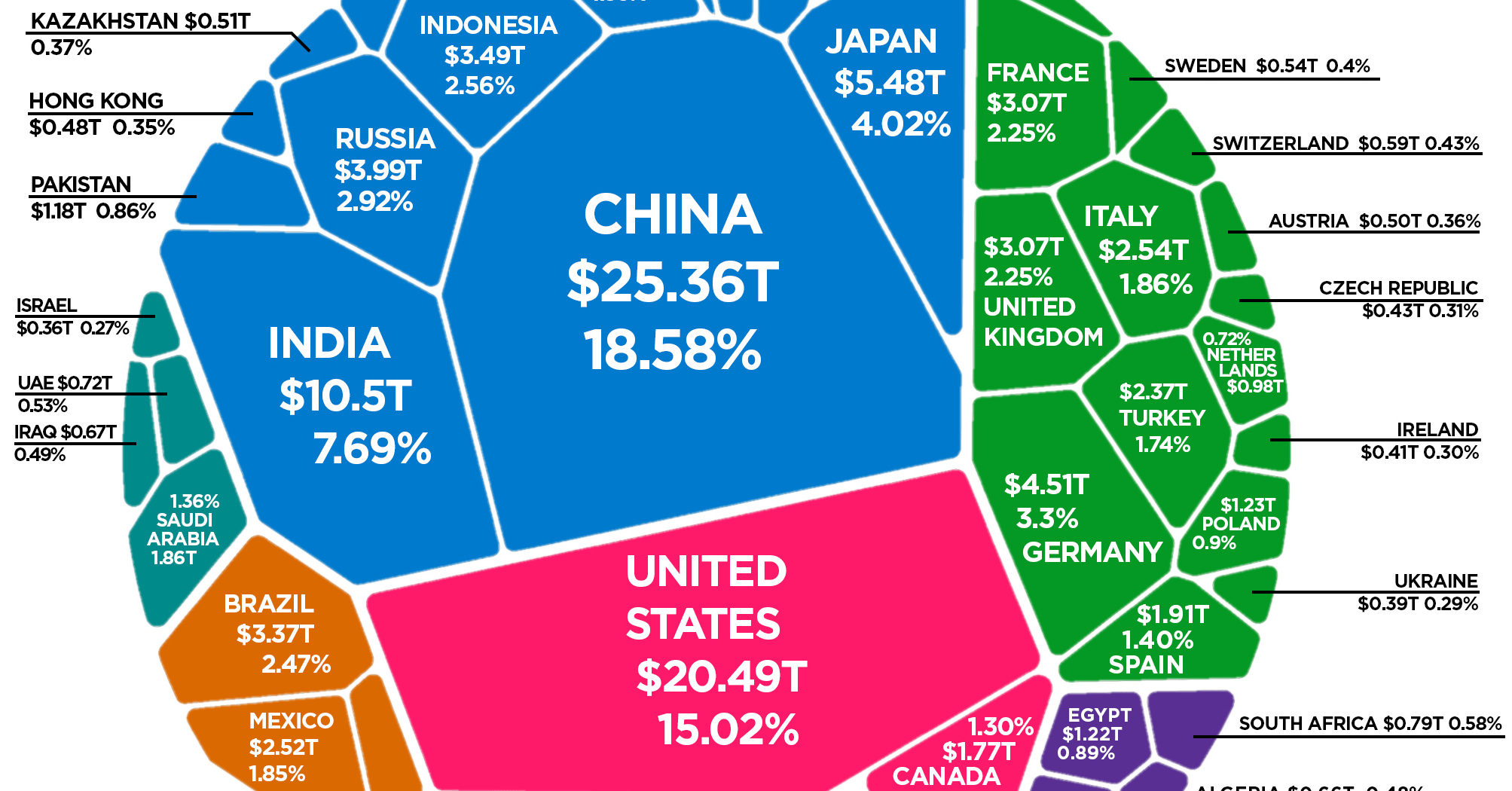
The Composition of the World Economy by GDP (PPP)
/gdp-increase-636251500-c69345ee97ba4db99375723519a2c1bd.jpg)
Real Gross Domestic Product (Real GDP) Definition

The World Economy in One Chart: GDP by Country