Decoding Iran's Economic Pulse: A Deep Dive Into Its GDP Trajectory
Understanding a nation's economic health often begins with a close look at its Gross Domestic Product (GDP). For Iran, a country frequently in the global spotlight due to its geopolitical significance and unique economic structure, its GDP data offers crucial insights into its performance, resilience, and challenges. Delving into Iran's GDP data in current US dollars, as meticulously provided by the World Bank, allows us to paint a clearer picture of its economic journey, shedding light on both its achievements and the hurdles it faces on the path to sustained prosperity.
This comprehensive analysis will explore the latest figures, historical trends, and the underlying factors shaping Iran's economic landscape. From its position in the global economy to the nuances of its per capita income and future projections, we aim to provide a detailed, accessible, and authoritative overview of Iran's GDP, helping you navigate the complexities of its economic narrative.
Table of Contents
- What is Gross Domestic Product (GDP)?
- Iran's GDP in 2023: A Snapshot
- Historical Trajectories: Iran's GDP Over Recent Years
- GDP Per Capita: A Measure of Individual Prosperity
- Iran's Economic Classification and Global Competitiveness
- Projections for 2024: What Lies Ahead for Iran's Economy?
- The Broader Economic Landscape: Challenges and Opportunities
- Navigating Iran's Economic Data: A Prudent Approach
What is Gross Domestic Product (GDP)?
Before diving into Iran's specific figures, it's essential to understand what GDP truly represents. Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is one of the most fundamental indicators used to gauge the health and size of an economy. At its core, GDP at purchaser's prices is the sum of gross value added by all resident producers in the economy plus any product taxes and minus any subsidies not included in the value of the products. In simpler terms, it's the total monetary value of all finished goods and services produced within a country's borders in a specific time period, usually a year or a quarter.
- Iran Times
- Israeli Iran News
- Iran Medals In Olympics 2024
- Trump Iran Nuclear Deal
- Iran Launches Attack On Israel
GDP serves as a comprehensive scorecard for a nation's economic output. It helps policymakers, investors, and the public understand whether an economy is expanding or contracting, and how productive its various sectors are. While a high GDP doesn't automatically translate to high living standards for all citizens, it is generally correlated with economic opportunity and national prosperity. For a nation like Iran, whose economy is subject to various internal and external pressures, tracking its GDP provides critical insights into its resilience and development trajectory.
Iran's GDP in 2023: A Snapshot
The latest available official data from the World Bank indicates that the gross domestic product (GDP) in Iran was worth 404.63 billion US dollars in 2023. This figure positions Iran as a notable, albeit relatively smaller, player on the global economic stage. To put this into perspective, the GDP value of Iran represents 0.38 percent of the entire world economy, highlighting the country's contribution to global output.
Beyond the raw nominal figure, understanding the growth rate provides a more dynamic view of economic performance. In 2023, Iran's GDP growth rate was 5.04%. This positive growth represents a substantial change of 24.662 billion US dollars over 2022. It's important to note that this growth rate typically refers to real GDP, which accounts for inflation, providing a clearer picture of actual economic expansion. For context, real GDP in 2022 was $488.865 billion. This robust growth rate in 2023 suggests a period of recovery or expansion for the Iranian economy, despite ongoing challenges.
- Iran On The World Map
- Us Vs Iran War Who Would Win
- Why Do Iran Hate Israel
- Iran And Syria
- Islamism In Iran
Nominal vs. Real GDP: Understanding the Nuances
When discussing GDP figures, it's crucial to distinguish between nominal and real GDP. Nominal GDP measures economic output at current market prices, meaning it includes the effects of inflation or deflation. Real GDP, on the other hand, adjusts for price changes, providing a more accurate measure of the actual volume of goods and services produced. The data provided for Iran often presents both, which can sometimes appear contradictory if not interpreted carefully.
For instance, while the nominal GDP for 2023 was reported as $404.63 billion, the real GDP for 2022 was $488.865 billion, with a 5.04% growth in 2023. If we apply the 5.04% growth to the 2022 real GDP, the 2023 real GDP would be approximately $513.48 billion ($488.865 billion * 1.0504). The difference between this calculated real GDP and the reported nominal GDP of $404.63 billion for 2023 can be attributed to significant deflation or currency depreciation against the US dollar. This highlights the complex interplay of production, inflation, and exchange rates in shaping Iran's economic indicators and underscores the importance of looking beyond single figures to grasp the full economic picture.
Historical Trajectories: Iran's GDP Over Recent Years
Iran's economic journey has been marked by periods of both significant growth and contraction, reflecting its sensitivity to global oil prices, international sanctions, and domestic policies. Looking at recent history provides valuable context to its current standing. For example, Iran's GDP for 2021 was 359.10 billion US dollars, which represented a substantial 49.79% increase from 2020. This surge suggests a strong rebound after a challenging period.
Conversely, Iran's GDP for 2020 was 239.74 billion US dollars, a stark 15.48% decline from 2019. This contraction in 2020 can be largely attributed to the compounding effects of intensified sanctions and the global economic slowdown caused by the COVID-19 pandemic. These figures vividly illustrate the volatility inherent in Iran's economic performance, making it a dynamic case study for economic resilience and adaptation.
Factors Influencing Iran's Economic Volatility
The pronounced swings in Iran's GDP are not random; they are often the direct result of a confluence of powerful factors. Chief among these are international sanctions, particularly those targeting its vital oil and banking sectors. These sanctions restrict Iran's ability to export its primary commodity and engage in global financial transactions, severely impacting its revenue streams and access to international markets. The significant decline in 2020, for instance, correlates strongly with the re-imposition and tightening of such measures.
Beyond sanctions, global oil price fluctuations play a massive role. As a major oil producer, Iran's economy is heavily reliant on hydrocarbon exports. A drop in oil prices can quickly diminish national income, affecting government spending, investment, and overall economic activity. Domestically, government policies, structural economic reforms (or lack thereof), and issues like inflation and unemployment also contribute to the economic climate. Furthermore, geopolitical tensions and regional stability can influence investor confidence and trade routes, adding another layer of complexity to Iran's economic narrative. The interplay of these internal and external forces creates the characteristic volatility observed in Iran's GDP figures.
GDP Per Capita: A Measure of Individual Prosperity
While total GDP provides an aggregate measure of economic output, GDP per capita offers a more granular insight into the average standard of living and economic well-being of a country's population. It's calculated by dividing the total GDP by the country's population. In the Islamic Republic of Iran, with a population of 90,608,707 people, the GDP per capita was $5,668 in 2023. This figure represents a modest increase of $207 from $5,461 in 2022, signifying a change of 3.8% in GDP per capita year-on-year.
Despite this recent increase, Iran's position globally in terms of GDP per capita has seen a decline. In fact, Iran has fallen to 117th place globally in terms of GDP per capita. This ranking suggests that while the overall economy may be growing, the distribution of wealth or the sheer size of the population relative to its output means that individual prosperity, on average, lags behind many other nations. This metric is crucial for understanding the everyday economic realities faced by Iranian citizens.
Beyond GDP Per Capita: The Legatum Prosperity Index
While GDP per capita is a useful economic indicator, it doesn't capture the full spectrum of human well-being and societal development. More nuanced assessments often provide a richer picture. The Legatum Prosperity Index, for example, offers a more comprehensive evaluation by considering various structural components of prosperity, including economic quality, business environment, governance, education, health, safety and security, personal freedom, social capital, and natural environment. This holistic approach provides a broader understanding of a nation's overall well-being.
Iran's position in the Legatum Prosperity Index further reflects the country’s unfavourable situation, ranking 126th out of 167 countries. This significantly lower ranking compared to its GDP per capita position suggests that while economic output might be present, other crucial aspects of societal prosperity—such as governance, personal freedoms, or social capital—may be lagging. This index underscores that true national well-being extends beyond mere economic figures and encompasses a wide array of factors that contribute to a flourishing society.
Iran's Economic Classification and Global Competitiveness
The International Monetary Fund (IMF) classifies Iran as a transition economy. This classification means that Iran is in the process of changing from a centrally planned economy to a market-oriented economy. Such a transition typically involves significant structural reforms, privatization, liberalization of markets, and the establishment of institutions conducive to a market economy. This ongoing transformation inherently brings both opportunities for growth and significant challenges, as the economy adapts to new frameworks and global competitive pressures.
In terms of global competitiveness, Iran's standing has seen shifts. In 2014, the World Economic Forum's analysis of the global competitiveness of 144 countries ranked Iran 83rd. This position, while not top-tier, indicated a certain level of competitive capacity at the time. However, the dynamics of global competitiveness are constantly evolving, and a country's ranking can be influenced by factors such as innovation, infrastructure, market efficiency, and institutional strength. For a transition economy like Iran, improving global competitiveness requires sustained efforts in economic diversification, technological advancement, and integration into the global economy, often complicated by external constraints.
Projections for 2024: What Lies Ahead for Iran's Economy?
Looking ahead, projections for Iran's economy in 2024 suggest continued, albeit perhaps moderating, growth. The gross domestic product of Iran is projected to grow by 3.5% in 2024 compared to last year. This positive growth forecast indicates an expectation of continued economic activity and potentially further recovery. However, it's crucial to note that economic projections are subject to various internal and external factors, including geopolitical developments, oil price volatility, and the effectiveness of domestic economic policies.
In terms of nominal value, the GDP figure in 2024 is projected to be approximately $401,357 million (or €370,921 million). Interestingly, while a 3.5% growth is projected (likely real GDP growth), this nominal figure is slightly lower than the reported 2023 nominal GDP of $404.63 billion. This discrepancy further highlights the difference between real growth (which accounts for actual production increases) and nominal value (which can be affected by currency fluctuations and deflation/inflation). Despite this, Iran is positioned at number 41 in the ranking of GDP among the 196 countries for which data is published, indicating its significant size in absolute terms on the world stage.
Interpreting Future Economic Signals
Interpreting future economic signals for Iran requires a careful balance of optimism and realism. The projected 3.5% real GDP growth for 2024 is a positive sign, suggesting that the underlying productive capacity of the economy continues to expand. This growth could be driven by various factors, including increased oil production (if sanctions ease or workarounds are found), non-oil sector development, or domestic consumption. However, the slight decrease in projected nominal GDP compared to 2023's nominal figure suggests that factors like currency depreciation against the dollar or persistent inflationary pressures might continue to impact the perceived value of its economic output.
For investors and analysts, these signals imply a complex environment. While there might be opportunities arising from real economic expansion, the nominal value fluctuations and the ongoing geopolitical landscape introduce considerable risk. The 41st global ranking in terms of total GDP underscores Iran's economic weight, but its lower rankings in per capita GDP and broader prosperity indices remind us that overall size doesn't automatically translate to widespread individual well-being or a robust, diversified economy. Future economic performance will heavily depend on how Iran navigates its internal reforms and external relations, particularly regarding sanctions and regional stability.
The Broader Economic Landscape: Challenges and Opportunities
Iran's economic landscape, as revealed by its GDP data, is one of considerable complexity and dynamism. The consistent volatility in its GDP, as seen in the sharp decline in 2020 followed by a robust recovery in 2021 and continued growth into 2023 and 2024, underscores its resilience but also its vulnerability to external shocks and internal policy shifts. The challenge lies in converting this growth into sustainable, inclusive prosperity for its large population, reflected in the relatively low GDP per capita ranking.
Opportunities for Iran's economy primarily lie in its vast natural resources, particularly oil and gas, and its large, young, and educated population. Diversification away from oil dependence, investment in non-oil sectors like manufacturing,
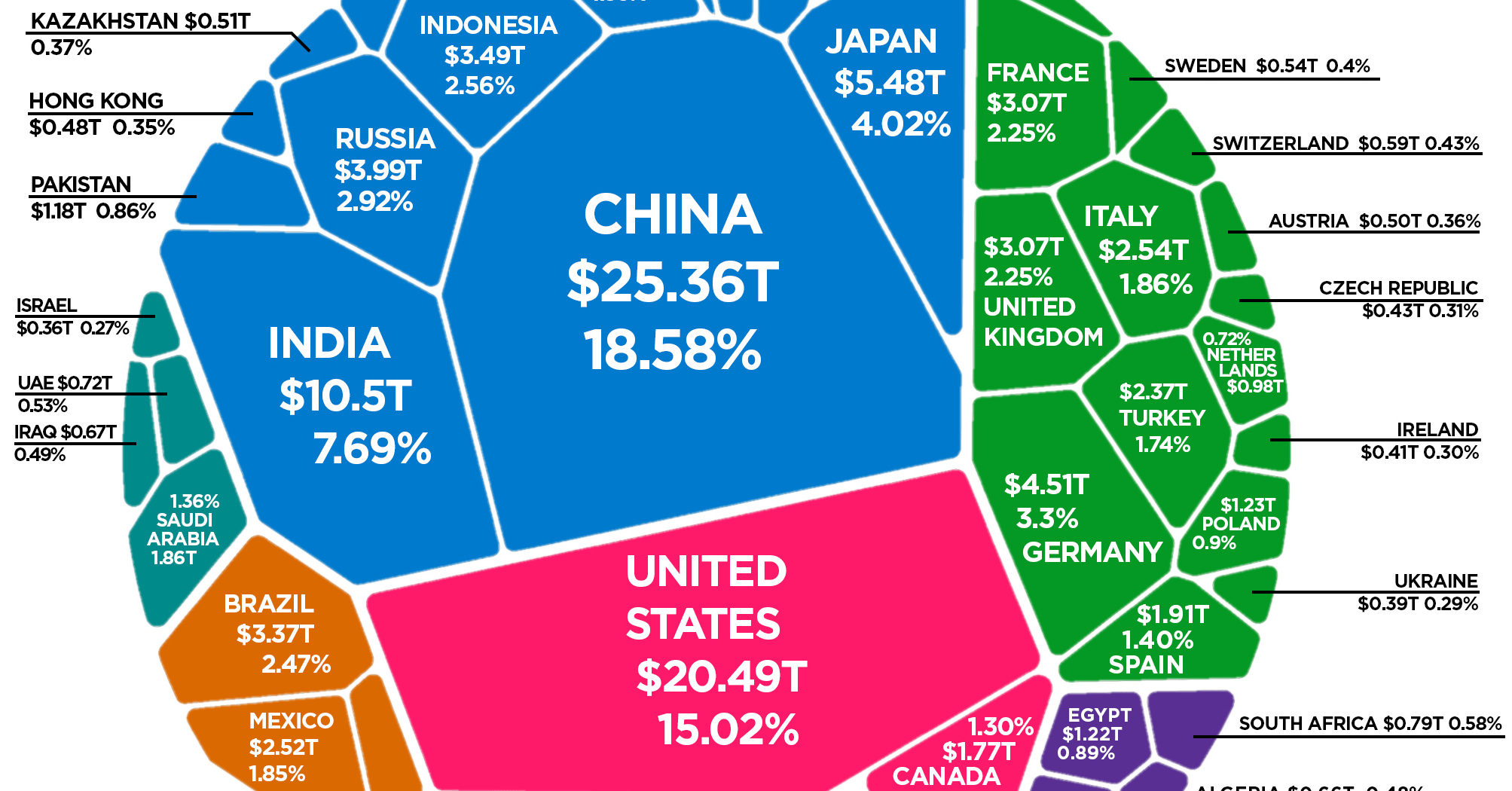
The Composition of the World Economy by GDP (PPP)
/gdp-increase-636251500-c69345ee97ba4db99375723519a2c1bd.jpg)
Real Gross Domestic Product (Real GDP) Definition

The World Economy in One Chart: GDP by Country