Iran's GDP: Unpacking Economic Growth & Economic Challenges
Understanding a nation's economic pulse often begins with its Gross Domestic Product (GDP). For Iran, this vital economic indicator tells a compelling story of resilience, challenge, and shifting global dynamics. Far from being just a number, Iran's GDP reflects the intricate interplay of internal policies, international relations, and the daily lives of its over 90 million people. This article delves deep into the latest data, historical trends, and future projections for Iran's economy, providing a comprehensive overview that is crucial for anyone seeking to grasp the complexities of this significant Middle Eastern nation.
Exploring Iran's GDP data, primarily sourced from authoritative bodies like the World Bank and the International Monetary Fund (IMF), offers invaluable insights into its economic performance. From the nuances of its sectoral contributions to the broader implications of geopolitical pressures, we aim to demystify the figures and present a clear picture of where Iran stands economically and what lies ahead.
Table of Contents
- Understanding GDP: What It Means for Iran
- Iran's GDP: A Historical Snapshot (1960-2023)
- Recent Trends in Iran's GDP (2019-2023)
- GDP Per Capita: A Closer Look at Individual Prosperity
- Sectoral Contributions to Iran's GDP
- The Geopolitical Shadow: Sanctions and Oil Prices
- Reliable Data: Sources and Methodologies
- Conclusion: Charting Iran's Economic Path Forward
Understanding GDP: What It Means for Iran
Gross Domestic Product (GDP) serves as the primary gauge of a country's economic health. It represents the total monetary value of all finished goods and services produced within a country's borders in a specific time period. For a nation like Iran, whose economy is often subject to external pressures and internal policy shifts, understanding its GDP provides critical insights into its overall productivity, living standards, and capacity for growth. Analyzing Iran's GDP helps policymakers, investors, and the general public comprehend the economic landscape.
When we talk about Iran's GDP, we are looking at a complex economic system that has navigated significant headwinds over the decades. The figures provided by the World Bank, IMF, and the Central Bank of Iran offer a window into this resilience and the ongoing challenges. These numbers are not just abstract statistics; they reflect the daily economic activities, trade flows, and investment decisions that shape the nation's financial well-being.
Defining GDP: The World Bank's Perspective
The World Bank defines "GDP at purchaser's prices" as the sum of gross value added by all resident producers in the economy plus any product taxes and minus any subsidies not included in the value of the products. This comprehensive definition ensures that the reported GDP figures capture the full scope of economic activity within a country. For Iran, this means accounting for everything from oil production and agricultural output to the burgeoning services sector and manufacturing industries.
The gross domestic product (GDP) in Iran was worth 404.63 billion US dollars in 2023, according to official data from the World Bank. This figure represents a significant portion of the nation's economic output and serves as a benchmark for its standing in the global economy. Understanding this definition is crucial for accurately interpreting the data and appreciating the scale of Iran's economic endeavors.
Iran's GDP: A Historical Snapshot (1960-2023)
To truly appreciate the current state of Iran's GDP, it's essential to look at its historical trajectory. Economic data for the Islamic Republic of Iran, specifically gross domestic product in current prices, has been meticulously graphed and made available by the World Bank (IRNNGDPDUSD) from 2000 to 2025. Furthermore, broader historical data for the gross domestic product (MKTGDPIRA646NWDB) is available from 1960 to 2023, providing a long-term perspective on Iran's economic evolution.
Over these decades, Iran's economy has faced numerous challenges, ranging from international sanctions to fluctuations in oil prices and instability in economic policies. These external and internal factors have significantly influenced the nation's economic performance, leading to periods of robust growth, as well as contractions. The long-term data series highlights the cyclical nature of Iran's economy, often heavily influenced by global energy markets and geopolitical developments.
Recent Trends in Iran's GDP (2019-2023)
Focusing on more recent years, Iran's GDP figures reveal a dynamic and at times volatile economic environment. The period from 2019 to 2023 has been particularly eventful, marked by significant shifts in growth rates and overall economic output. These trends provide a clear indication of the immediate challenges and opportunities facing Iran's economy.
The Surge of 2021 and the 2020 Decline
The years leading up to and including the COVID-19 pandemic presented a mixed bag for Iran's economy. According to an April 2020 World Economic Outlook by the IMF, the GDP of Iran contracted in FY 2018 and FY 2019. However, a modest rebound was expected in 2020/2021. This expectation was partially met, albeit with some significant fluctuations.
- Iran GDP for 2020 was 239.74 billion US dollars, representing a 15.48% decline from 2019. This contraction can largely be attributed to the compounding effects of severe international sanctions and the initial impact of the global pandemic on trade and economic activity.
- In stark contrast, Iran GDP for 2021 was 359.10 billion US dollars, marking a substantial 49.79% increase from 2020. This remarkable surge indicates a strong rebound, possibly driven by a combination of adapting to sanctions, some domestic policy adjustments, and a recovery in global oil prices. This significant growth highlights the potential for rapid recovery when conditions align, showcasing the underlying resilience of Iran's economy.
Iran's Economic Standing in 2022 and 2023
Moving into more recent years, Iran continued to demonstrate economic activity and growth, solidifying its position within the global economic landscape, despite persistent challenges.
- Iran, Islamic Republic, held a strong economic position in 2022 with a GDP of 413.49 billion USD, ranking 34th globally. This placed Iran just behind Bangladesh, which had a GDP of 460.20 billion USD, indicating Iran's significant economic scale on the world stage.
- The gross domestic product (GDP) in Iran was worth 404.63 billion US dollars in 2023, according to official data from the World Bank. This figure for Iran's GDP represents 0.38 percent of the world economy, illustrating its proportional contribution to global economic output.
- The GDP growth rate in 2023 was 5.04%, representing a change of 24,662,000,000 US$ over 2022, when real GDP was $488,865,000,000. This continued growth rate in 2023, following the strong rebound in 2021, suggests a period of sustained, albeit modest, economic expansion for Iran. It's also important to note the distinction between nominal (current) GDP and real (constant, inflation-adjusted) GDP. Nominal (current) gross domestic product (GDP) of Iran was $404,626,000,000 (USD) as of 2023, while real GDP (constant, inflation adjusted) of the Islamic Republic of Iran reached $513,527,000,000 in 2023. The real GDP figure provides a more accurate picture of economic growth by removing the effects of inflation.
GDP Per Capita: A Closer Look at Individual Prosperity
While overall GDP provides a macro-level view of a nation's economy, GDP per capita offers a more granular insight into the average economic output per person. This metric is particularly important for understanding the living standards and economic well-being of a country's population.
For the Islamic Republic of Iran, with a population of 90,608,707 people, the GDP per capita figures reveal ongoing development:
- GDP per capita in 2023 was $5,668. This figure represents an increase of $207 from $5,461 in 2022, signifying a positive change of 3.8% in GDP per capita. This incremental growth suggests a slight improvement in the average economic share for each individual in Iran.
- In 2022, the GDP per capita for Iran was 4669.57 USD, placing it at 115th position globally, trailing behind Indonesia with a GDP per capita of 4787.99 USD. While this ranking indicates that Iran still has significant room for improvement in terms of individual prosperity compared to many other nations, the upward trend in 2023 is a positive sign.
These figures for GDP per capita in current US dollars for Iran, Islamic Republic, are also provided by the World Bank, underscoring their reliability for economic analysis.
Sectoral Contributions to Iran's GDP
Understanding the composition of Iran's GDP by sector provides valuable insights into the structure of its economy and its key drivers. While Iran is widely known for its vast oil and gas reserves, its economy is increasingly diversified, with other sectors playing significant roles.
The biggest sector of Iran's economy is services, which accounts for 51 percent of GDP. This highlights a modernizing economy where the service industry contributes more than half of the total economic output. Within the services sector, several important segments stand out:
- Real estate and specialized and professional services: These combined account for 14 percent of total GDP. This indicates a robust property market and a growing demand for specialized expertise, reflecting urban development and business expansion.
- Trade, restaurants, and hotels: This segment contributes 12 percent to GDP. This points to the importance of domestic commerce, tourism (when conditions allow), and hospitality services in the Iranian economy.
- Public services: Accounting for 10 percent of GDP, public services underscore the significant role of the government in providing essential services and employment, typical of many economies with a strong state presence.
While these figures emphasize the growing importance of the service sector, it's crucial to remember that the energy sector, particularly oil and gas, remains a critical component of Iran's economy, especially in terms of export revenues and foreign exchange generation. However, the diversification into services shows a broader base for Iran's GDP.
The Geopolitical Shadow: Sanctions and Oil Prices
It is impossible to discuss Iran's GDP without acknowledging the profound impact of geopolitical developments, particularly international sanctions and fluctuations in global oil prices. Iran's economy has faced numerous challenges in recent decades, ranging from international sanctions to fluctuations in oil prices and instability in economic policies. These external pressures have often constrained economic growth, limited foreign investment, and impacted the nation's ability to fully integrate into the global economy.
The tightening or easing of foreign sanctions through diplomatic negotiations is closely tied to Iran's economic future. Sanctions directly affect Iran's ability to export oil, access international financial markets, and import essential goods and technologies. This, in turn, impacts government revenues, inflation, and the overall business environment. The Central Bank of Iran, along with World Bank staff calculations, closely monitors these dynamics, including exchange rates and inflation, as they are direct consequences of geopolitical pressures.
The reliance on oil revenues also makes Iran's GDP vulnerable to the volatile nature of global oil markets. When oil prices are high, Iran benefits significantly, boosting its foreign reserves and enabling greater government spending. Conversely, drops in oil prices can severely strain the economy, exacerbating the effects of sanctions and leading to economic contractions. The constant interplay of these factors makes forecasting Iran's economic performance particularly challenging.
Future Outlook: Navigating 2024 and 2025
Looking ahead, the outlook for Iran's GDP remains heavily influenced by these persistent geopolitical and economic factors. The present article analyzes the state of Iran's economy at the start of 2025, especially in relation to global and regional trends. While there have been periods of growth, the path forward is fraught with uncertainties.
- Gross domestic product of Iran grew 3.5% in 2024 compared to last year. The GDP figure in 2024 was €370,921 million, equivalent to approximately $401,357 million. This growth, while positive, is still modest compared to the potential of Iran's economy if it were fully integrated into global markets. Iran is number 41 in the ranking of GDP of the 196 countries that we publish, indicating its continued presence as a significant, albeit constrained, economic player.
- However, the outlook for Iran's economy in 2025 is grim. As pressures mount, the pace of Iran's energy collapse will only accelerate. This stark prediction underscores the ongoing challenges, particularly concerning the energy sector, which remains crucial for the nation's economic stability and export earnings. The potential easing or tightening of foreign sanctions through diplomatic negotiations will be the primary determinant of whether this grim outlook can be mitigated or exacerbated.
The dual challenges of external pressures and the need for internal economic reforms mean that while Iran's GDP shows signs of resilience, its full potential remains untapped, contingent on a complex web of international relations and domestic policy choices.
Reliable Data: Sources and Methodologies
The integrity and accuracy of economic data are paramount, especially when discussing a nation as geopolitically significant as Iran. The data presented in this article, particularly concerning Iran's GDP, is primarily drawn from highly reputable and authoritative sources. These include:
- The World Bank: A leading international financial institution that provides financial and technical assistance to developing countries worldwide. The World Bank offers extensive economic data, including GDP in current US dollars for Iran, Islamic Republic, and GDP per capita. Their estimates for Iran's GDP are available since 1960 in nominal terms and since 1990 in PPP (Purchasing Power Parity) terms at current and constant prices.
- The International Monetary Fund (IMF): An organization of 190 countries, working to foster global monetary cooperation, secure financial stability, facilitate international trade, promote high employment and sustainable economic growth, and reduce poverty around the world. The IMF's World Economic Outlook reports often provide crucial insights and projections for Iran's economy.
- The Central Bank of Iran: The national bank of Iran, responsible for monetary and banking policies, and the collection of national economic statistics. Their staff calculations, often in conjunction with World Bank staff, contribute to the official data.
These institutions employ rigorous methodologies for data collection and analysis, ensuring the trustworthiness and expertise behind the figures. For instance, data for gross domestic product in current prices for Iran, Islamic Republic of (IRNNGDPDUSD) is available for graphing and download from 2000 to 2025, covering aspects about Iran, REO (Regional Economic Outlook), and GDP. Similarly, gross domestic product data for the Islamic Republic of Iran (MKTGDPIRA646NWDB) is available from 1960 to 2023. Such extensive historical and projected data series allow for robust analysis and a deeper understanding of Iran's economic trajectory.
Conclusion: Charting Iran's Economic Path Forward
The journey through Iran's GDP figures reveals a narrative of an economy marked by significant resilience, periods of impressive growth, and persistent challenges. From the substantial 49.79% surge in 2021 following a sharp decline in 2020, to its consistent contribution as 0.38% of the world economy, Iran's economic footprint is undeniable. The shift towards services as the largest sector, contributing 51% of GDP, highlights a diversifying economy, moving beyond its traditional reliance on oil, though the energy sector remains critically important.
Despite these internal strengths, the overarching influence of international sanctions and the volatility of global oil prices continue to cast a long shadow over Iran's economic prospects, particularly evident in the "grim" outlook for 2025. The nation's GDP per capita, while showing modest increases, still indicates room for significant improvement in individual prosperity.
Understanding Iran's GDP is not merely an academic exercise; it is crucial for anyone seeking to comprehend the nation's geopolitical role, investment potential, and the daily realities faced by its citizens. The data, meticulously compiled by institutions like the World Bank and IMF, paints a picture of an economy constantly adapting and striving for growth amidst a complex global environment. As Iran continues to navigate these intricate dynamics, its economic performance will undoubtedly remain a focal point for regional and international observers.
What are your thoughts on Iran's economic future? Do you believe the service sector can fully offset the challenges in the energy sector? Share your insights in the comments below, and explore more articles on global economic trends on our site.
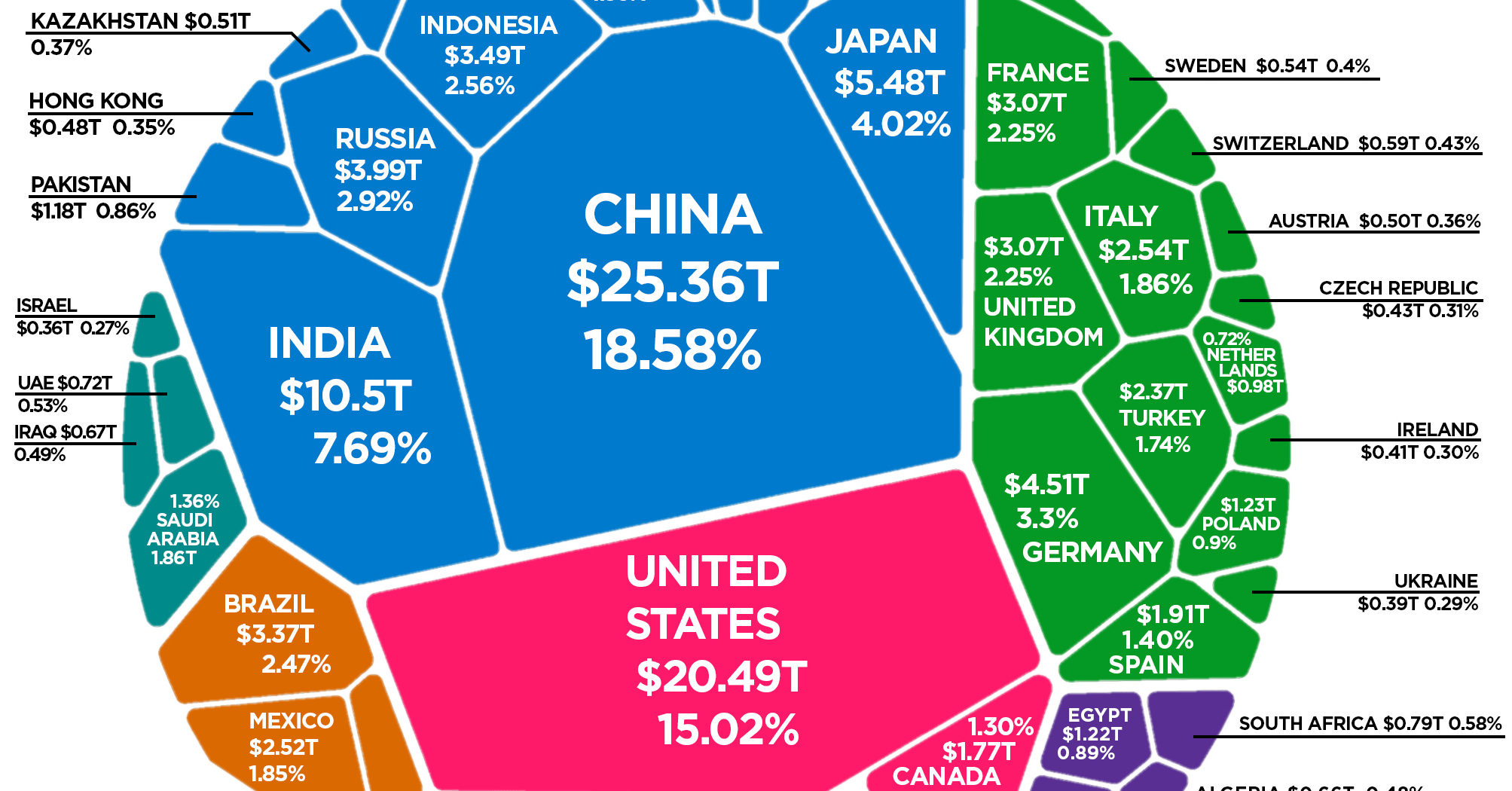
The Composition of the World Economy by GDP (PPP)
/gdp-increase-636251500-c69345ee97ba4db99375723519a2c1bd.jpg)
Real Gross Domestic Product (Real GDP) Definition

The World Economy in One Chart: GDP by Country