Navigating Iran's Digital Landscape: Information Systems Unveiled
The complex world of information systems in Iran is a fascinating yet often misunderstood realm, deeply intertwined with the nation's technological aspirations, geopolitical realities, and societal dynamics. From the foundational enterprises shaping its digital infrastructure to the intricate web of cybersecurity measures and the pervasive influence of state control, understanding Iran's information systems requires a nuanced perspective. This article delves into the various facets of this evolving landscape, shedding light on key players, strategic objectives, and the tangible impact on daily life and international relations.
Beyond the headlines, Iran's engagement with information technology extends across diverse sectors, including healthcare, national security, and public administration. While facing unique challenges, including international sanctions and internal pressures, the country continues to develop and deploy sophisticated IT solutions. This exploration aims to provide a comprehensive overview, grounded in factual insights, to illuminate the intricate workings and broader implications of information systems within Iran.
Table of Contents
- The Foundations of Iranian IT: ISIRAN's Legacy
- Information Systems and National Security: A Dual-Edged Sword
- The Digital Iron Curtain: Control and Censorship
- Advancements in Healthcare Information Systems
- Governing Cyberspace: Regulatory Bodies and Oversight
- The International Dimension: Sanctions and Global Implications
- Cultivating Expertise: IT Education in Iran
- The Evolving Landscape: Challenges and Future Outlook
The Foundations of Iranian IT: ISIRAN's Legacy
At the heart of Iran's technological development lies a foundational entity, ISIRAN. This organization, whose full name is Information Systems IRAN, has played a pivotal role in shaping the nation's information technology landscape for decades. Established in 1971, ISIRAN emerged as a key player in the nascent IT sector, laying the groundwork for subsequent digital advancements. Its longevity and continued involvement underscore its significance in Iran's technological evolution.
- Iran President Assassinated
- Iran Biden
- Isreal And Iran War
- Who Is President In Iran
- Mellat Park Tehran Iran
ISIRAN is not merely an independent IT company; it is deeply integrated into Iran's industrial and defense complex. The company has been a subsidiary of Iran Electronics Industries (IEI Co.), a major conglomerate involved in various electronic and defense-related manufacturing. This affiliation provides ISIRAN with a unique position, linking its commercial IT endeavors with broader strategic interests of the state. Understanding ISIRAN's role is crucial for comprehending the broader architecture of information systems in Iran.
A Historical Perspective: From 1971 to Today
Since its inception in 1971, ISIRAN has evolved significantly, adapting to changing technological paradigms and geopolitical circumstances. Its establishment marked an early recognition by Iranian authorities of the importance of information technology for national development. Over the decades, ISIRAN has likely contributed to various public and private sector IT projects, from data processing to network infrastructure development. Its connection to Iran Electronics Industries (IEI Co.) suggests a focus on hardware and integrated systems, complementing software and service development. This long history positions ISIRAN as a veteran in the field of information systems in Iran, having witnessed and participated in the country's journey from rudimentary computing to more sophisticated digital environments.
Information Systems and National Security: A Dual-Edged Sword
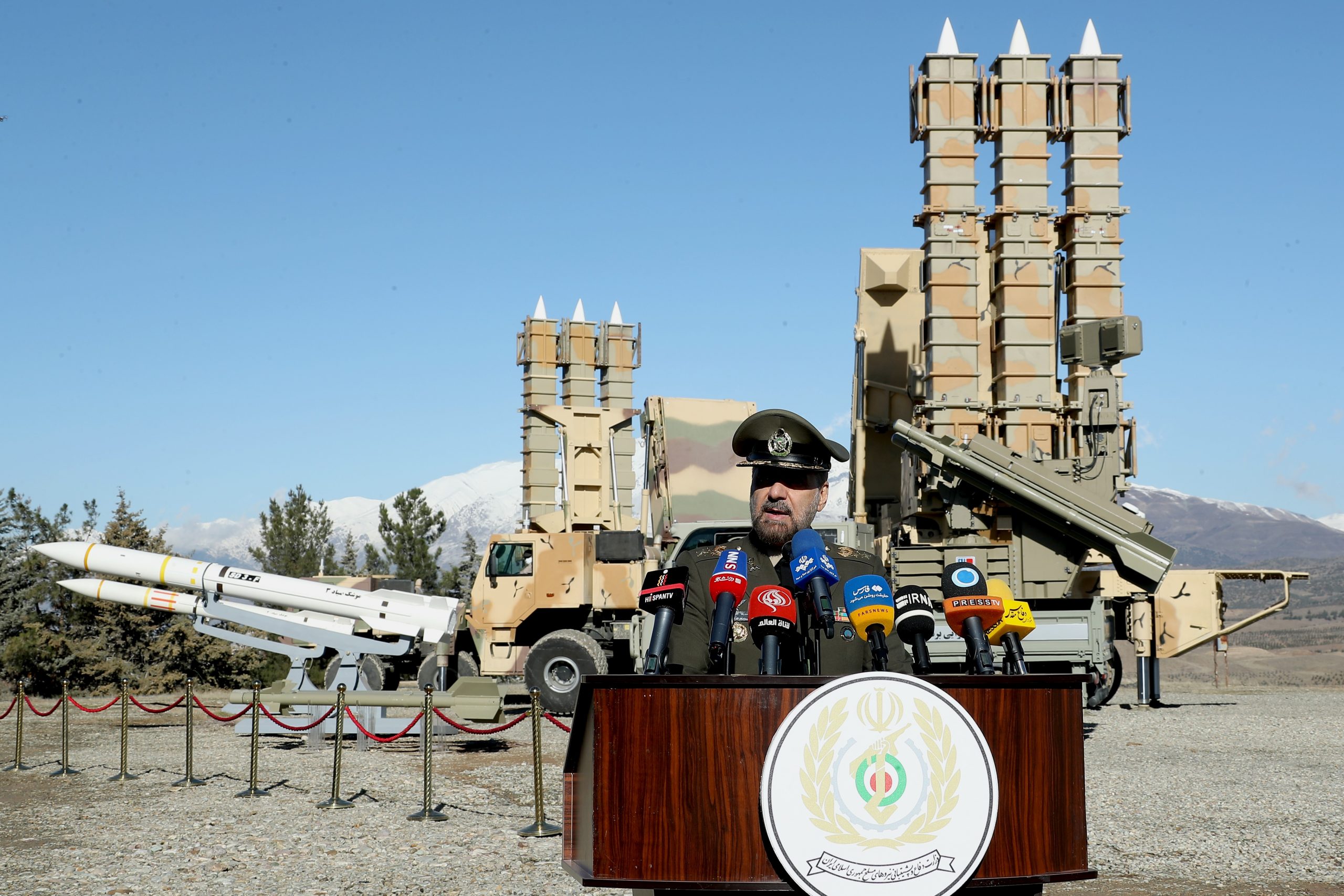
The role of information systems in Iran's national security strategy cannot be overstated. These systems serve as both critical infrastructure for defense and a potent tool in the realm of cyber warfare and intelligence. According to the U.S., ISIRAN itself is affiliated with Iran's Ministry of Defense and Armed Forces Logistics (MODAFL), underscoring the direct link between civilian IT development and military objectives. This affiliation highlights how seemingly commercial information systems can be leveraged for strategic purposes, reflecting a broader trend where technology becomes an integral part of national defense and offense.
- Iran Attack Israel Israeli News
- World Atlas Iran
- Type Of Government Iran
- Iran Missleattack
- Air Force Iran
Iran's national security strategy, stated broadly, rests on two fundamental pillars: deterrence and resilience. Information systems play a crucial role in both. Deterrence involves projecting capabilities, including cyber offensive capabilities, to dissuade potential adversaries. Resilience, on the other hand, focuses on protecting critical infrastructure and maintaining operational continuity in the face of threats. The development and deployment of robust information systems are essential for achieving these strategic goals, enabling the country to manage its defense assets, secure its communications, and respond to external pressures.
Cyber Offensive Capabilities and Strategic Pillars
An analysis of Iran's cyber offensive capabilities highlights a structured approach to leveraging information systems for strategic advantage. This involves understanding the organizational structure, the underlying strategy, and the global efforts to counter these threats. As the cybersecurity landscape continues to evolve, detailed analyses of Iran's cyber threat actors, their tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs), and their most recent campaigns become critical. These actors often target information systems outside of Iran, aiming to gather intelligence, disrupt operations, or exert influence. The development of these capabilities is intrinsically linked to the nation's broader defense posture, utilizing information systems as a key component of its non-conventional warfare toolkit.
The strategic pillars underpinning these capabilities extend beyond mere defense. While protecting its own digital assets, Iran also employs its cyber capabilities for offensive purposes, aiming to damage information systems abroad. This dual-use nature of information systems technology—for both defense and offense—makes it a central component of Iran's national security apparatus. The continuous evolution of cyber threats necessitates ongoing development and adaptation of these systems, reflecting a dynamic and high-stakes environment where digital prowess is a significant factor in international relations.
The Digital Iron Curtain: Control and Censorship
Beyond national security, information systems in Iran are also extensively used for domestic control and censorship. Iranian authorities have meticulously observed and learned from other digital authoritarian regimes, notably China, to refine their own methods of internet control. This learning process has led to significant improvements in related technologies, enabling the regime to exercise greater dominion over the internet and attempt to construct a digital firewall around internet users in Iran. This "firewall" aims to restrict access to certain content and platforms, thereby shaping the information environment accessible to its citizens.
While dissident voices continue to find ways to be heard, the ruling regime has undeniably intensified its campaign of control in cyberspace. This intensification is part of a broader cyber suppression strategy, often referred to as "soft war," which seeks to curtail the free flow of information through the internet. The primary objective of this strategy is to prevent the widespread dissemination of foreign ideas, culture, and influences that are perceived as threats to the established order. This involves a sophisticated array of technical measures, including filtering, blocking, and surveillance, all reliant on advanced information systems.
Mastering Digital Authoritarianism
The mastery of digital authoritarianism in Iran is a testament to the strategic deployment of information systems. The government's approach is multifaceted, combining technical controls with legal and social pressures. By building a robust infrastructure for surveillance and censorship, authorities can monitor online activities, identify and suppress dissent, and control narratives. This involves deep packet inspection, content filtering, and the development of national intranet alternatives to global internet services. The goal is to create a controlled information ecosystem where the state dictates what information is accessible and how it is consumed. This systematic use of information systems for control has profound implications for freedom of expression and access to information for Iranian citizens, making the digital space a critical battleground for civil liberties.
Advancements in Healthcare Information Systems
Despite the challenges and controversies surrounding other aspects of information systems in Iran, the healthcare sector has seen notable positive developments. The implementation of health information systems (HIS) has significantly impacted the efficiency and quality of healthcare services. For instance, a study evaluated surgery information systems that were subsystems of two prominent health information systems developed by Tirazheh and Peyvand Dadeh. These systems are currently deployed in a substantial number of educational hospitals across Iran—236 and 67 hospitals, respectively—demonstrating a widespread adoption of digital solutions in medical facilities.
The positive effects of these implementations are tangible. They have demonstrably improved the speed and accuracy of various working procedures and activities within hospitals. Examples include streamlining the ordering process for medical supplies and tests, and enhancing patient information recording and retrieval. These improvements are achieved by facilitating accessibility to information for medical staff, increasing the accuracy of documentation, and accelerating administrative and clinical workflows. The successful integration of such information systems highlights Iran's commitment to modernizing its healthcare infrastructure, leveraging technology to enhance patient care and operational efficiency, even amidst broader technological constraints.
Governing Cyberspace: Regulatory Bodies and Oversight
The governance of cybersecurity and information systems in Iran is a complex undertaking, involving several regulatory bodies, each with distinct responsibilities. These organizations collectively play a crucial role in ensuring the safety, integrity, and controlled evolution of the nation's digital infrastructure. Their mandate extends from setting technical standards and issuing licenses to monitoring compliance and responding to cyber incidents. The fragmented nature of this oversight reflects the multifaceted challenges posed by a rapidly evolving digital landscape, particularly one with significant national security implications.
Among the most prominent organizations in this regulatory framework is the Information Technology Organization of Iran (ITO). Operating under the Ministry of Communications and Information Technology, the ITO is tasked with a broad range of responsibilities related to IT development, policy formulation, and cybersecurity. Its role is central to coordinating efforts across different sectors, promoting digital literacy, and fostering innovation within the IT ecosystem, while also ensuring adherence to national policies regarding data security and internet control. The presence of such dedicated bodies underscores the strategic importance Iran places on managing its information systems effectively, balancing development with security and control.
The International Dimension: Sanctions and Global Implications
The international landscape significantly impacts the development and operation of information systems in Iran, particularly through the imposition of sanctions. The U.S. Department of the Treasury's Office of Foreign Assets Control (OFAC) maintains a Specially Designated Nationals and Blocked Persons (SDN) List, which serves as a critical reference tool providing factual notice of OFAC's actions regarding designated nationals and other persons. This list is designed to block the assets of individuals and entities that are deemed to pose a threat to U.S. national security or foreign policy.
Notably, the organization Information Systems Iran (ISIRAN) has been included in this list of special purpose citizens and persons to be blocked. This designation carries significant implications, restricting its ability to engage in international transactions and access certain technologies. Such sanctions directly affect the procurement of hardware, software, and services from international markets, compelling Iranian entities to develop indigenous solutions or rely on alternative, often less efficient, supply chains. The inclusion of key players like ISIRAN on the SDN list underscores the geopolitical tensions that shape Iran's technological trajectory, making the development of robust and self-reliant information systems a national imperative.
Cultivating Expertise: IT Education in Iran
Recognizing the critical importance of human capital in the digital age, Iran has invested in cultivating expertise in the field of information technology. The country's universities offer a range of programs, including master's degrees in IT, to train the next generation of professionals. These educational institutions play a vital role in developing the skills necessary to design, implement, and manage complex information systems. Students can find various master's degrees in the field of Information Technology (IT) from top universities across Iran, covering diverse specializations such as software engineering, network security, data science, and IT management.
This focus on higher education in IT is crucial for several reasons. Firstly, it provides a domestic talent pool, reducing reliance on foreign expertise, especially in the face of international sanctions. Secondly, it fosters research and development, contributing to the innovation of new technologies and solutions tailored to Iran's specific needs and challenges. Finally, it supports the continuous evolution of information systems within the country, ensuring that the workforce is equipped to handle emerging technologies and cybersecurity threats. The emphasis on IT education reflects a long-term strategic vision to build a self-sufficient and technologically capable nation.
The Evolving Landscape: Challenges and Future Outlook
The landscape of information systems in Iran is characterized by a dynamic interplay of domestic innovation, geopolitical pressures, and strategic objectives. The country faces unique challenges, including the need to circumvent international sanctions, combat sophisticated cyber threats, and manage the delicate balance between technological advancement and state control over information. Despite these hurdles, Iran continues to push forward, developing indigenous solutions and fostering a growing IT sector.
The future outlook for information systems in Iran will likely be shaped by several factors: the ongoing evolution of global cybersecurity threats, the impact of international relations on technology transfer, and the internal dynamics between technological progress and governmental control. As Iran seeks to enhance its digital capabilities, the emphasis will remain on building resilient, secure, and domestically controlled information infrastructure. The journey of information systems in Iran is a testament to the nation's determination to carve out its own digital destiny, navigating a complex web of technological, political, and social forces.
Conclusion
In summary, the world of information systems in Iran is a multifaceted domain, encompassing foundational companies like ISIRAN, strategic national security initiatives, pervasive internet control, and vital advancements in sectors like healthcare. We've explored how entities like ISIRAN, with its historical roots and affiliations to defense ministries, play a dual role in both commercial IT and national security. The intricate balance between developing cyber offensive capabilities and implementing robust censorship mechanisms highlights the state's comprehensive approach to managing its digital space.
Furthermore, the positive impact of health information systems and the structured regulatory environment demonstrate a commitment to technological progress in specific sectors. However, the international dimension, particularly U.S. sanctions affecting organizations like Information Systems Iran, underscores the external pressures shaping the country's technological trajectory. As Iran continues to invest in IT education and navigate these complexities, its digital landscape will undoubtedly remain a subject of significant global interest. We encourage you to share your thoughts on these developments in the comments below or explore other articles on our site that delve into similar topics of technology and geopolitics.
- Iran Tv 24
- How Much Money Did Obama Give Iran
- Israel War With Iran
- Traditional Iran Clothes
- Will United States Go To War With Iran

Iran Introduced Two New Air Defense Systems - IHA News

Iran Unveils Two Homegrown Air Defense Systems - Iran Front Page
The Map of Iran coloring page - Download, Print or Color Online for Free