Unveiling Iran's Continent: A Deep Dive Into Its Asian Identity
Have you ever wondered, "What continent is Iran in?" It's a question that often arises due to Iran's unique geopolitical and cultural position, frequently associated with the "Middle East." While the Middle East is a distinct region, it's crucial to understand its continental placement. The definitive answer is that Iran is located in the continent of Asia.
This article will explore Iran's precise geographical coordinates, its extensive borders, its rich historical and cultural ties within Asia, and why understanding its continental identity is more significant than just a simple geographical fact. We will delve into the nuances of its location, from its vast land area to its diverse natural landscapes, firmly establishing Iran's undeniable presence within the Asian continent.
Table of Contents
- The Definitive Answer: Iran's Place on the Global Map
- More Than Just a Continent: Iran's Geographical Context
- Historical and Cultural Significance Within Asia
- The Middle East Connection: A Region Within a Continent
- Understanding Iran's Coordinates: Latitude and Longitude
- Diverse Landscapes: Iran's Natural Wonders
- Tehran: The Capital City's Asian Roots
- Why This Matters: The Importance of Geographical Understanding
The Definitive Answer: Iran's Place on the Global Map
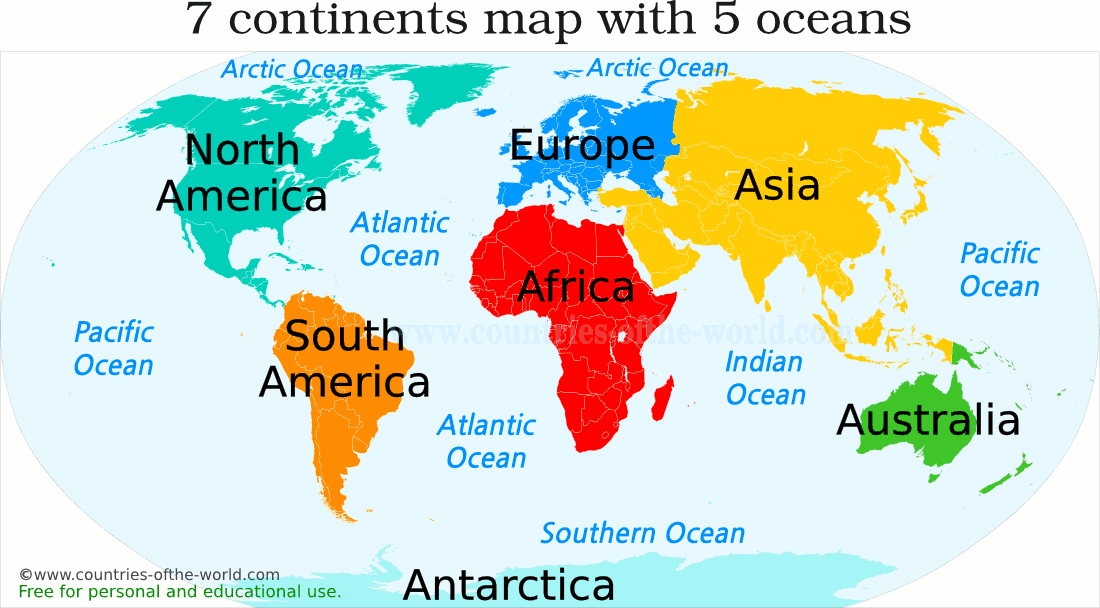
When pinpointing the exact location of countries, clarity is paramount. For Iran, the question of "what continent is Iran in" is unequivocally answered: it is situated in Asia. More specifically, it occupies a significant portion of Western Asia, a region that serves as a crucial bridge between Europe, Africa, and the broader Asian landmass. This geographical positioning has profoundly shaped Iran's history, culture, and geopolitical role throughout millennia.
- Beautiful Women From Iran
- Iran Assassination Trump
- Israel And Iran War News
- Israel Attack Iran Today
- Milad Tower Iran
Officially known as the Islamic Republic of Iran (IRI), and historically recognized as Persia, this nation stands as a testament to ancient civilizations and modern complexities. Its location within Asia is not merely a label but a foundational aspect of its identity, influencing everything from its climate to its trade routes and its interactions with neighboring countries. Understanding this continental placement is the first step in appreciating the full scope of Iran's global significance.
Western Asia: A Precise Location
To be even more precise, Iran is found in Western Asia, sometimes referred to as Southwest Asia. This region is a subregion of Asia, characterized by its diverse geography, rich history, and significant role in global affairs. Other nations commonly considered part of Western Asia include Iraq, Turkey, Saudi Arabia, and many others in the Arabian Peninsula and the Levant. Iran's presence in this particular part of Asia places it at a historical crossroads, where ancient empires rose and fell, and where major trade routes, such as the Silk Road, once flourished.
The geographical boundaries of Western Asia are often debated, but Iran consistently falls within all definitions. This precise placement means Iran shares many characteristics with its regional neighbors, yet it also maintains a distinct identity shaped by its unique Persian heritage and vast territorial expanse. Its location in Western Asia is key to understanding its strategic importance and its historical interactions with both Eastern and Western powers.
- Black People In Iran
- Iran Israel War
- Ministry Of Foreign Affairs Iran
- Iran Country Pictures
- Iran Drone Ship
More Than Just a Continent: Iran's Geographical Context
Beyond simply stating "Iran is in Asia," it's vital to delve into the broader geographical context that defines this nation. Its size, its borders, and its relationship with the surrounding regions all contribute to a comprehensive understanding of where Iran truly lies on the world map. This context helps explain why Iran is such a diverse and historically significant country within the Asian continent.
Size and Scale: Iran in the Middle East
Iran is not just another country in Asia; it is a nation of considerable scale. By land area, Iran is the second largest country in the Middle East. Its approximate area is a staggering 1,648,195 square kilometers. To put this into perspective, this vast territory encompasses an incredible range of climates and topographies, from arid deserts to lush forests and towering mountain ranges. This immense size contributes significantly to its internal diversity and its strategic importance in the region.
The sheer scale of Iran's landmass means it shares extensive borders with numerous countries, creating a complex web of geopolitical relationships. This vastness also means that different parts of Iran experience vastly different environmental conditions, supporting a wide array of ecosystems and human settlements. The country's large size is a defining feature that sets it apart from many of its smaller neighbors in the Middle East, solidifying its status as a major player within the Asian landscape.
Bordering Nations: Iran's Extensive Neighbors
One of the most telling aspects of Iran's geographical location within Asia is the impressive list of countries it shares borders with. These extensive borders highlight its central position in Western Asia and its historical role as a nexus of trade, culture, and sometimes, conflict. Understanding these neighbors helps paint a clearer picture of Iran's continental context:
- To the west, Iran borders Iraq.
- To the northwest, it shares borders with Turkey, Azerbaijan, and Armenia.
- To the north, it is bordered by the Caspian Sea, the world's largest inland body of water.
- To the northeast, it borders Turkmenistan.
- To the east, Iran shares a frontier with Afghanistan and Pakistan.
- To the southeast, it extends to the Gulf of Oman.
- To the south, it is bordered by the Persian Gulf, a vital waterway for global oil trade.
This extensive network of borders underscores Iran's pivotal position. Its access to the Caspian Sea in the north and the Persian Gulf and Gulf of Oman in the south provides crucial maritime routes, while its land borders connect it to Central Asia, the Caucasus, the Levant, and the Indian subcontinent. This intricate geopolitical tapestry is a direct consequence of where Iran is located in the continent of Asia, making it a critical hub for regional and international relations.
Historical and Cultural Significance Within Asia
Iran's continental identity is not just a matter of lines on a map; it's deeply interwoven with its rich history and vibrant culture. Historically known as Persia, Iran boasts one of the world's oldest continuous civilizations, with a heritage that has profoundly influenced the broader Asian continent and beyond. Its location in Asia has allowed it to serve as a melting pot of ideas, religions, and artistic expressions.
The Persian civilization, which predates many modern nations, left an indelible mark on the regions spanning from Egypt to India. This historical legacy is a testament to Iran's deep roots within Asia. Furthermore, the adoption and spread of Islamic heritage from the 7th century onwards further cemented Iran's cultural ties within the continent, particularly with other Islamic nations in Asia and the Middle East. Its unique identity, a blend of ancient Persian traditions and Islamic influences, contributes significantly to the cultural diversity of Asia.
From the architectural marvels of Isfahan to the poetic traditions of Rumi and Hafez, Iran's cultural contributions are intrinsically linked to its Asian context. Its art, music, literature, and philosophical thought have resonated across the continent, influencing neighboring cultures and establishing Iran as a cultural powerhouse within Asia. This cultural richness is a direct reflection of its long and storied past, firmly anchored in the Asian landmass.
The Middle East Connection: A Region Within a Continent
A common point of confusion when discussing Iran's location is its association with the "Middle East." It's important to clarify that the Middle East is a geopolitical and cultural region, not a continent itself. Culturally and geographically, Iran is indeed part of the Middle East, which is traditionally considered a region within the continent of Asia. This distinction is crucial for understanding the nuances of Iran's global positioning.
The term "Middle East" emerged from a Eurocentric perspective, referring to the lands between Europe and the "Far East." It encompasses countries primarily in Western Asia and parts of North Africa. Iran's inclusion in this region is due to shared cultural, historical, and often religious ties with its neighbors, particularly its strong Islamic heritage and its position at the crossroads of major civilizations. However, this regional classification does not alter its continental affiliation.
Therefore, while Iran is a prominent country in the Middle East, this regional designation simply refines its location within the larger Asian continent. It helps to contextualize its political dynamics, economic relationships, and cultural exchanges within a specific sub-region of Asia, rather than suggesting it belongs to a separate continental landmass. This dual identity – a key player in the Middle East and an integral part of Asia – provides a more complete picture of Iran's place in the world.
Understanding Iran's Coordinates: Latitude and Longitude
For a precise geographical understanding of where Iran is located, one can turn to its GPS coordinates. These numerical values provide an exact fix on its position on the Earth's surface, leaving no doubt about its continental home. The latitudinal coordinate of Iran is approximately 32.4279° N. This means Iran is situated above the equator, firmly placing it in the Northern Hemisphere.
More broadly, the country lies between latitudes 25° and 40° N, and longitudes 44° and 63° E. These coordinates confirm its placement in the northern temperate zone and its eastward position relative to the Prime Meridian. The specific combination of these coordinates clearly defines Iran's location within the vast expanse of the Asian continent. These precise measurements are fundamental for cartographers, navigators, and anyone seeking an exact geographical understanding of the nation.
The latitudinal range also explains the varied climates experienced across Iran, from the subtropical Caspian Sea coast in the north to the arid desert regions further south. The longitudinal spread, meanwhile, dictates its time zone and its proximity to various cultural and economic centers within Asia. These coordinates are not just abstract numbers; they are the scientific bedrock that confirms Iran's undeniable position as an Asian country.
Diverse Landscapes: Iran's Natural Wonders
The vast territory of Iran, nestled within the Asian continent, is home to an astonishing array of natural landscapes and biodiversity. Its geography varies dramatically from rugged mountains, such as the Alborz and Zagros ranges, to vast deserts like the Dasht-e Kavir and Dasht-e Lut. This incredible topographical diversity is a direct consequence of its substantial size and its specific location within Asia, spanning various climatic zones.
Iran's varied nature and climate contribute to an abundant and diverse population of plants and animals, truly amazing in both number and variety compared to many other parts of the world. For instance, the Iranian vegetation diversity is more than twice the size of the entire European continent and nearly equals that of the Indian subcontinent. This rich ecological tapestry, from dense forests in the north to unique desert ecosystems, underscores the natural wealth contained within this Asian nation.
This natural diversity is not just a point of interest; it has historically shaped human settlement patterns, agricultural practices, and cultural expressions. The mountains have provided natural defenses and resources, while the fertile plains have supported ancient civilizations. The deserts, though harsh, have fostered unique forms of adaptation and resilience. All these natural features are integral to understanding the physical landscape of Iran as a key component of the Asian landmass.
Tehran: The Capital City's Asian Roots
The capital city of Iran is Tehran, a sprawling metropolis situated in the northern part of the country. As the political, economic, and cultural heart of the nation, Tehran's location further solidifies Iran's identity within the Asian continent. Located at the foot of the majestic Alborz Mountains, Tehran is a vibrant hub that showcases the blend of modernity and tradition characteristic of many major Asian cities.
Tehran's position in northern Iran, close to the Caspian Sea and bordering regions like Azerbaijan and Turkmenistan, highlights its strategic importance within Asia. It serves as a gateway to the central Asian steppes and has historically been a significant point on trade routes connecting East and West. The city's growth and development are intrinsically linked to Iran's overall trajectory within the continent, reflecting its evolving role in regional and global affairs.
From its bustling bazaars to its contemporary skyscrapers, Tehran embodies the dynamism of an Asian capital. Its cultural institutions, educational centers, and economic activities are all rooted in the context of a major Asian nation. The very existence and prominence of Tehran serve as a tangible reminder of where Iran is located, firmly anchored in the vast and diverse continent of Asia.
Why This Matters: The Importance of Geographical Understanding
Understanding the precise continental location of a country like Iran goes far beyond mere academic curiosity. It is fundamental to comprehending its geopolitical significance, its historical trajectory, its cultural identity, and its role in international relations. Knowing that Iran is located in the continent of Asia, specifically Western Asia, provides a crucial framework for interpreting global events and fostering informed perspectives.
For instance, understanding Iran's borders with nations like Iraq, Afghanistan, and Pakistan, or its access to vital waterways like the Persian Gulf, illuminates its strategic importance in energy trade and regional security. Its historical ties to ancient Persian civilization and its deep Islamic heritage, both developed within the Asian context, explain much about its current societal values and foreign policy. Even the mention of Israel, often in the news for geopolitical tensions with Iran, is contextualized by its own location at the crossroads of Asia, Africa, and Europe, emphasizing the interconnectedness of these regions within the broader Asian sphere.
In a world increasingly shaped by global interactions, accurate geographical knowledge is a cornerstone of literacy. Dispelling misconceptions about "what continent is Iran in" allows for a clearer understanding of its place in the world, fostering more nuanced discussions about its challenges, contributions, and future. It reinforces the fact that Iran is an integral and influential part of the Asian continent, with a rich tapestry of history, culture, and natural beauty that continues to unfold.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the question of "what continent is Iran in" has a clear and definitive answer: Iran is located in the continent of Asia. More specifically, it is a prominent country in Western Asia, a region that forms a vital bridge between various parts of the world. Officially known as the Islamic Republic of Iran, and historically as Persia, this nation is the second largest in the Middle East by land area, encompassing approximately 1,648,195 square kilometers.
Its extensive borders with countries like Iraq, Turkey, Azerbaijan, Armenia, Turkmenistan, Afghanistan, and Pakistan, along with its access to the Caspian Sea, Persian Gulf, and Gulf of Oman, underscore its strategic geographical importance within Asia. Culturally, Iran is deeply rooted in its Asian identity, shaped by ancient Persian civilization and a rich Islamic heritage that has profoundly influenced the continent. From its precise GPS coordinates to the diverse landscapes that characterize its vast territory, every aspect of Iran's geography points to its undeniable position as an integral part of Asia.
We hope this comprehensive article has provided you with a clear and detailed understanding of Iran's continental identity. Do you have further questions or insights about Iran's unique geographical and cultural standing? Feel free to leave a comment below and share your thoughts. For more in-depth explorations of global geography and culture, be sure to browse our other articles!

Vector Map of World Bathymetry Continents | One Stop Map | World map
7 continents of the world and their countries

Printable Map of the 7 Continents - Free Printable Maps